Primary cilia and their role in preeclampsia
- PMID: 40765552
- PMCID: PMC12320799
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.114433
Primary cilia and their role in preeclampsia
Abstract
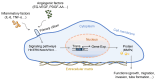
Preeclampsia is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy characterized by chronic placental ischemia and systemic maternal organ damage. The placenta is rich in blood vessels containing various types of cells, and preeclampsia is now widely accepted as a placenta-derived disease. Although the primary cilium regulates many diseases, its role in preeclampsia has not been comprehensively studied. Therefore, we conducted a review to provide valuable insights into the current understanding of the pathogenesis of preeclampsia, especially as related to the primary cilium, and to provide direction for new research objectives. Primary cilia are sensory microtubule-based organelles that translate extracellular clues into intracellular signals for molecular and cellular responses. They are crucial for the regulation of vascular development and have various mechanisms, such as epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, reaction to mechanical stress, and mediation of signal transduction. Dysfunction of the primary cilia contributes to aberrant fluid sensing or signal transduction, resulting in vascular disorders. Here, we summarize that angiogenic factors or inflammatory cytokines change the biological behaviors and functions of placental cells in preeclampsia by altering the length or signaling function of primary cilia. We further outline the role of the primary cilia in vascular endothelial function and other female reproductive disorders. Further research is needed to understand the underlying mechanisms and clinical treatment of primary ciliary deficiency in preeclampsia.
Keywords: placenta; preeclampsia; primary cilia; signaling transduction; vascular development..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Wu P, Haththotuwa R, Kwok CS, Babu A, Kotronias RA, Rushton C, Preeclampsia and Future Cardiovascular Health: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2017. 10. - PubMed
-
- Caropreso L, de Azevedo Cardoso T, Eltayebani M, Frey BN. Preeclampsia as a risk factor for postpartum depression and psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2020;23:493–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

