Cardiovascular and brain effects of liraglutide in transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) mice models
- PMID: 40765557
- PMCID: PMC12320650
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.112264
Cardiovascular and brain effects of liraglutide in transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTR) mice models
Abstract
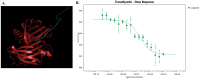
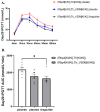
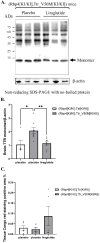
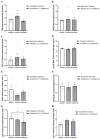
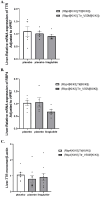
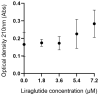
Aim: The effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (ATTRv) remain uncertain. This study aims to investigate whether liraglutide interacts with transthyretin protein (TTR) and thereby exerts therapeutic effects for ATTRv. Methods: High throughput screening was conducted to characterize the drug targets of liraglutide, and microscale thermophoresis was used to observe direct binding of liraglutide to TTR. Humanized RBP4/TTR (normal)and RBP4/TTRVal50Met (ATTRv) mice were constructed, and treated with liraglutide (0.3mg/kg/d) or placebo for 28 days. Fasting plasma glucose, intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT), and plasma brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) were measured. Brain and cardiac tissues were processed with western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and pathological staining to evaluate the lesion status in corresponding organs. Results: Liraglutide exhibited high affinity and direct combination ability to TTR. In ATTRv mice, liraglutide significantly decreased the contents of TTR protein in brain compared with placebo. However, the cardiovascular prognosis measurements including heart failure (plasma BNP concentrations), cardiac fibrosis (the relative expression levels of Cola1 and TGFβ1 in cardiac tissues), and pathological changes (right ventricular collagen percentage, ventricular septum thickness, left ventricular wall thickness, and left ventricular internal diameter) were statistically comparable between mice receiving liraglutide and placebo treatment. Conclusion: Liraglutide could decrease the deposition of TTR in brain tissues, while it did not improve cardiovascular outcomes in ATTRv mice compared to placebo. More researches regarding the mechanisms and therapeutic effects of GLP-1RAs to ATTRv are still required.
Keywords: ATTRv; brain; heart failure; liraglutide; transthyretin amyloidosis polyneuropathy; transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: L.J. has received fees for lecture presentations and for consulting from AstraZeneca, Merck, Metabasis, MSD, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, and Takeda. All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf (available on request from the corresponding authors) and declare no other support from any organization for the submitted work other than that described above.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dapagliflozin treatment and cardiovascular outcome in RBP4/TTRVal30Met (transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis) mice.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Feb;11(1):179-188. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14567. Epub 2023 Oct 25. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 37877450 Free PMC article.
-
Transthyretin variants impact blood-nerve barrier and neuroinflammation in amyloidotic neuropathy.Brain. 2025 Jul 7;148(7):2537-2550. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf028. Brain. 2025. PMID: 39874259
-
Effects of Patisiran, an RNA Interference Therapeutic, on Cardiac Parameters in Patients With Hereditary Transthyretin-Mediated Amyloidosis.Circulation. 2019 Jan 22;139(4):431-443. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035831. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 30586695 Clinical Trial.
-
Biomarkers in Subclinical Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2025 Feb 13;22(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s11897-025-00696-y. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2025. PMID: 39945945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unravelling the myriad physiologic roles of transthyretin: critical considerations for treating transthyretin amyloidosis.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2536755. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2536755. Epub 2025 Jul 27. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40717228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

