Radiotherapy elicits immunogenic cell death and metabolic shifts in the tumor microenvironment: implications for immunotherapy
- PMID: 40765564
- PMCID: PMC12320787
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.109515
Radiotherapy elicits immunogenic cell death and metabolic shifts in the tumor microenvironment: implications for immunotherapy
Abstract
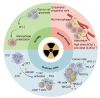
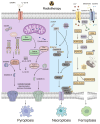
Radiotherapy, one of the most utilized strategies to combat malignancies, has been constantly explored for its effectiveness and optimized, and it is currently operating at the molecular level. The tumor microenvironment (TME), where complicated changes take place under radiotherapy and other treatments, inevitably draws our attention to metabolic alterations, immunogenic cell death (ICD) and immunological interactions. In response to radiotherapy, tumor metabolism promotes DNA and membrane repair processes and reduces oxidative stress, thereby collectively alleviating the occurrence of cell death. Moreover, the induction of pyroptosis, necroptosis and ferroptosis under radiotherapy has the potential to increase antitumor immunity. Therefore, comprehensive knowledge about how radiotherapy triggers these modalities of ICD mechanically is necessary for developing nanomedicines with more accurate targets. In addition, information on clinical advancements as well as the management of adverse events is important for investigating radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy. This review provides an overview of up-to-date findings on metabolic changes and ICD under radiotherapy and provides insight into the status of the TME.
Keywords: immunogenic cell death; immunotherapy; metabolism; radiotherapy; tumor microenvironment.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
From mitochondrial dysregulation to ferroptosis: Exploring new strategies and challenges in radioimmunotherapy (Review).Int J Oncol. 2025 Sep;67(3):76. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5781. Epub 2025 Aug 8. Int J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40776761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence of immunogenic cell death (ICD) and ICD-dependent dendritic cell activation induced by extracorporeal photopheresis in patients with leukaemic forms of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jul 17;193(2):276-286. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf102. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40112181
-
Harnessing Immunogenic Cell Death to Boost the Impact of Radiation Therapy.Cancer J. 2025 Jul-Aug 01;31(4):e0780. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000780. Epub 2025 Aug 11. Cancer J. 2025. PMID: 40768307 Review.
-
Nanoparticles induced cuproptosis to enhance antitumor immunotherapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 Jul 28;23(1):544. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03616-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40717092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new paradigm for cancer immunotherapy: targeting immunogenic cell death-related noncoding RNA.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 23;15:1498781. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1498781. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39916954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang K, Tepper JE. Radiation therapy-associated toxicity: Etiology, management, and prevention. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:437–54. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Huang D, Saw PE, Song E. Turning cold tumors hot: from molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. Trends Immunol. 2022;43:523–45. - PubMed
-
- Gerard CL, Delyon J, Wicky A, Homicsko K, Cuendet MA, Michielin O. Turning tumors from cold to inflamed to improve immunotherapy response. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021;101:102227. - PubMed
-
- Mittal A, Nenwani M, Sarangi I, Achreja A, Lawrence TS, Nagrath D. Radiotherapy-induced metabolic hallmarks in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer. 2022;8:855–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

