Identification of IGF2BP3 for the Expression and Prognosis in Gastrointestinal Cancers
- PMID: 40765570
- PMCID: PMC12320697
- DOI: 10.7150/ijms.114411
Identification of IGF2BP3 for the Expression and Prognosis in Gastrointestinal Cancers
Abstract
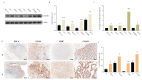
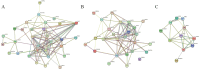
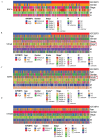
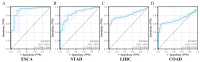
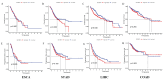
Purpose: This study investigates the expression, diagnostic, and prognostic significance of IGF2BP3 in gastrointestinal cancers, providing new insights for clinical management and patient care. Methods: An integrated approach was used to analyze the expression and mutation of IGF2BP3 across various cancers, utilizing multiple online analytical tools. Data from the TCGA database were examined to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in four types of gastrointestinal cancers and to assess the specific expression of IGF2BP3. Further validation was carried out through western blotting (WB), quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was also employed to investigate the relationships between IGF2BP3 and its associated genes. Additionally, bioinformatics databases were used to investigate the impact of IGF2BP3 on the diagnosis and prognosis of these cancers. Results: High expression of IGF2BP3 is a notable feature across these four gastrointestinal cancers, as demonstrated in public databases. Confirmation in cancer cells and tissues support this observation. Clinicopathological analysis reveals significant associations between IGF2BP3 expression and cancer stages in gastric cancer, and with cancer grades in liver cancer. The diagnostic accuracy of IGF2BP3 is found to be highest for esophageal cancer. Moreover, elevated IGF2BP3 levels correlate with poorer overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in liver cancer patients. Conclusions: This study underscores the significant expression of IGF2BP3 in gastrointestinal cancers and its potential value in both diagnostic and prognostic assessments. These findings could enhance diagnostic accuracy and support the development of targeted therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: IGF2BP3; diagnosis; gastrointestinal cancers; prognosis.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics identification and validation of m6A/m1A/m5C/m7G/ac4 C-modified genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1055. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14216-7. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597017 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis reveals NTN1 as an immune infiltrate risk factor and its potential prognostic value in SKCM.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3223. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-85444-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863609 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Wang S, Zheng R, Li J, Zeng H, Li L, Chen R. et al. Global, regional, and national lifetime risks of developing and dying from gastrointestinal cancers in 185 countries: a population-based systematic analysis of GLOBOCAN. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;9:229–37. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(23)00366-7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davila RE, Davila ML. Recent Advancements in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Cancers. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2022;51:xiii–xiv. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2022.07.009. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Lucero-Prisno DE 3rd, Zhang L, Xu W, Wong SH, Ng SC. et al. Updated epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers in East Asia. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;20:271–87. doi: 10.1038/s41575-022-00726-3. - PubMed
-
- Wen D, Xiao H, Gao Y, Zeng H, Deng J. N6-methyladenosine-modified SENP1, identified by IGF2BP3, is a novel molecular marker in acute myeloid leukemia and aggravates progression by activating AKT signal via de-SUMOylating HDAC2. Mol Cancer. 2024;23:116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02013-y. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

