Comparison of Infection-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Across Large-Scale Residual Samples From Blood Donors, Commercial Laboratories, and Health Checkups in Japan, 2023
- PMID: 40765712
- PMCID: PMC12321519
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf415
Comparison of Infection-Induced SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Across Large-Scale Residual Samples From Blood Donors, Commercial Laboratories, and Health Checkups in Japan, 2023
Abstract
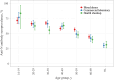
We compared severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 nucleocapsid antibody seroprevalence using 3 types of residual blood samples simultaneously collected in November-December 2023 from blood donors, commercial laboratories, and health checkups. Overall seroprevalence ranged from 53.5% to 58.8%, and notable variations were observed among the 30-39 and 50-59 age groups, highlighting the importance of multisource seroepidemiological surveillance.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; seroepidemiology; seroprevalence; surveillance.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: no reported conflicts.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

