Integrated Bioinformatics and Experimental Validation Reveal Macrophage Polarization-Related Biomarkers for Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
- PMID: 40765736
- PMCID: PMC12323875
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S537507
Integrated Bioinformatics and Experimental Validation Reveal Macrophage Polarization-Related Biomarkers for Osteoarthritis Diagnosis
Abstract
Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis and early detection is crucial to improving prognosis. In this study, we identified crucial genes associated with macrophage polarization in OA and constructed a diagnostic model to provide novel insights for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
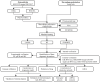
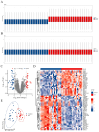
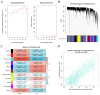
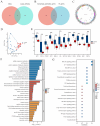
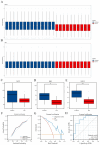
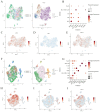
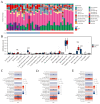
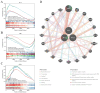
Methods: The GSE55235 and GSE55457 datasets were merged through the GEO database to identify genes related to macrophage polarization by conducting weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and differential expression analysis. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), random forest (RF), and support vector machine recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) algorithms were used to identify hub genes and construct a diagnostic model validated through internal datasets and multiple external bulk RNA-seq and single-cell RNA-seq data. Additionally, various analyses, including immune infiltration, gene set enrichment analysis, competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) construction, and drug prediction, were conducted. Finally, clinical samples were clinically validated through RT-qPCR (OA: Control = 10: 5) and IHC (6: 5) experiments.
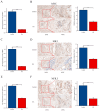
Results: Three hub genes (MYC, SIK1, and NFIL3) were identified, and the diagnostic model constructed using them demonstrated good diagnostic efficacy in both internal and external datasets (internal AUC = 0.965, external AUC = 0.847). In vitro experiments revealed that the hub genes in the synovial tissue of OA patients were significantly down-regulated (P < 0.01), confirming their potential as diagnostic biomarkers.
Conclusion: We constructed an OA diagnostic model related to macrophage polarization through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis, and the results indicated that these genes have high diagnostic value. However, further clinical studies and experimental assessments are needed to validate these findings.
Keywords: diagnostic model; machine learning; macrophage polarization; osteoarthritis.
© 2025 He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

