Beyond polarization: macrophage senescence in immunoregulation and cancer therapy
- PMID: 40765820
- PMCID: PMC12320033
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.115921
Beyond polarization: macrophage senescence in immunoregulation and cancer therapy
Abstract
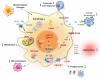
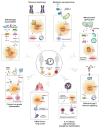
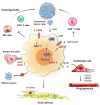
Cancer incidence is increasing globally, presenting significant health challenges due to its severe impact on morbidity and mortality. As a disease closely linked to aging, the prevalence of cancer is expected to increase with increasing age, underscoring the need for comprehensive research into its mechanisms and treatments. Macrophages, which are central to the immune system, play a paradoxical dual role in cancer progression. While they can suppress tumor growth, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) frequently facilitate tumor development and metastasis, a complexity that is further intricate by the aging process. As macrophages transition into senescent cells, they undergo changes, including shifts in cytokine profiles, reduced phagocytic activity, and altered metabolism. These senescent macrophages contribute to cancer progression by creating an immunosuppressive environment, promoting angiogenesis, and supporting tumor invasion. This review explores the intricate functions of senescent macrophages in cancer, highlighting their implications for tumor biology and their potential as therapeutic targets. We discuss strategies to manipulate senescent macrophages to enhance current cancer therapies, emphasizing the importance of understanding their mechanisms to advance cancer treatment.
Keywords: age-related diseases; cancer microenvironment; macrophage senescence; senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP); therapeutic targeting.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:12–49. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Yu S, Li X, Wen X, Liu S, Zu R. et al. Research progress on the interaction between oxidative stress and platelets: Another avenue for cancer? Pharmacol Res. 2023;191:106777. - PubMed
-
- Li S, Dong R, Kang Z, Li H, Wu X, Li T. Exosomes: Another intercellular lipometabolic communication mediators in digestive system neoplasms? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;73:93–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

