Treatment of severe bleeds with eptacog beta in hemophilia A or B with inhibitors: a post hoc analysis of the PERSEPT 1 and 2 trials
- PMID: 40765904
- PMCID: PMC12320391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bvth.2025.100069
Treatment of severe bleeds with eptacog beta in hemophilia A or B with inhibitors: a post hoc analysis of the PERSEPT 1 and 2 trials
Abstract
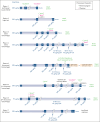
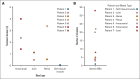
Severe bleeding episodes (BEs) in persons with hemophilia A or B and inhibitors (PwHABIs) represent challenging clinical situations and can require treatment regimens lasting days or weeks before hemostatic control is achieved. Eptacog beta is a recombinant activated human factor VII bypassing agent approved for treating and controlling bleeding in PwHABIs aged ≥12 years. The aim of this study is to assess the efficacy and safety of eptacog beta for severe bleed treatment in PwHABIs during 2 phase 3 trials (PERSEPT 1 and PERSEPT 2). Patients could treat severe BEs with initial doses of 75 or 225 μg/kg eptacog beta at home, followed by subsequent 75 μg/kg eptacog beta infusions administered at predefined intervals in a hospital or hemophilia treatment center. Satisfactory treatment responses to eptacog beta were typically defined in this post hoc analysis by physician- and patient-reported hemostasis evaluations of "excellent" or "good." Hemostatic control of an intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) in 1 patient was assessed by computed tomography. Seven PwHABIs (aged 1-50 years) treated 8 BEs considered severe or otherwise life threatening with eptacog beta during PERSEPT 1 and PERSEPT 2. Hemostatic control of 7 of these BEs (including 3 ICH events) was achieved. Eptacog beta treatment durations ranged from 25 minutes to 96 hours. No thrombotic events were reported, and eptacog beta was well tolerated. Most severe BEs resolved with eptacog beta treatment during PERSEPT 1 and PERSEPT 2. The PERSEPT 1 and PERSEPT 2 trials were registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02020369 and #NCT02448680, respectively.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: G.Y. has received consulting fees from ASC Biotherapeutics, BioMarin, Centessa, CSL Behring, Genentech/Roche, HEMA Biologics/LFB, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Sanofi, Genzyme, Spark, and Takeda; and funds for research support from Sanofi. J.M. has received research grants from BioMarin, Catalyst Biosciences, CSL Behring, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Spark, and uniQure; served as a consultant or member of the scientific board for BioMarin, CSL Behring, Catalyst Biosciences, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi, Spark, and Takeda; and received speaker bureau fees from the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH), Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and the World Federation of Hemophilia (WFH). L.N.B. has received research support from Pfizer, Bayer, Octapharma, Sanofi, Principia Biopharma, LFB, and HEMA Biologics; and consulting fees from Genentech, Genzyme, Novo Nordisk, and Octapharma. M.C. has received research support from Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; and honoraria for speaking/participating in advisory boards from Bayer, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda. Y.D. has received funding for research from CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk, LFB, Bayer, Centessa, Pfizer, and Octapharma; and acted as a paid consultant to Sobi, CSL Behring, Pfizer, Roche-Chugai, LFB, Takeda, Novo Nordisk, and Octapharma. M.E. has received grants and research funding from the American Thrombosis and Hemostasis Network (ATHN), uniQure, Takeda, Bayer, Sanofi Regeneron, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, and LFB; and honoraria and consulting fees from Takeda, Bayer, LFB, HEMA Biologics, BioMarin, Regeneron, Genentech/Roche, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, CSL Behring, Pfizer, Kedrion, the National Hemophilia Foundation (NHF; now known as the National Bleeding Disorders Foundation), and Magellan. A.G. has served as a consultant or advisory board member for Sanofi, HEMA Biologics, Vega Therapeutics, Alexion, and Genzyme; has been a member of Data and Safety Monitoring Committee for Adrenas; and has acted as a speaker for Sanofi, Alexion, and Genzyme. C.H. has received research funding from Bayer, BioMarin, CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Shire/Takeda, and Sobi; and honoraria and speaker bureau fees from Bayer, Belgium Red Cross Central Fractionation Facility (CAF-DCF), CSL Behring, Hoffmann-La Roche, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Shire/Takeda, Sobi, and uniQure. W.M. reports consultancy and research funding from Bayer, BioMarin, Biotest, CSL Behring, Chugai, Freeline, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sanofi, SOBI, and Takeda. D.N. has received consulting fees from HEMA Biologics. R.F.S. Jr has acted as a paid consultant for HEMA Biologics, LFB, Octapharma, Genentech/Roche, Bayer, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk, Guardian, Vega, Takeda, and Hemab; and has investigator-initiated grant funding from HEMA Biologics/LFB, Takeda, and Octapharma. M.W. has served on advisory boards for Bioverativ/Sanofi, Takeda, CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, Genentech, HEMA Biologics, Vega Therapeutics, and BioMarin; and served as a past investigator for HEMA Biologics and Novo Nordisk. S.W.P. has received grants/research support from Siemens and YewSavin; and served as a consultant to Apcintex, ASC Therapeutics, Bayer, BioMarin, CSL Behring, Equilibra Bioscience, GeneVentiv, HEMA Biologics, Freeline, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Poseida Therapeutics, Regeneron/Intellia, Roche/Genentech, Sanofi, Takeda, Spark Therapeutics, and uniQure. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Safety and Use of Eptacog Beta 225 µg/kg in Patients With Haemophilia A or B With Inhibitors.Haemophilia. 2025 Jul 17. doi: 10.1111/hae.70083. Online ahead of print. Haemophilia. 2025. PMID: 40674256
-
Pain Reduction Following Eptacog Beta Treatment of Bleeding Episodes in Adolescents and Adults With Haemophilia A or B Complicated by Inhibitors.Haemophilia. 2025 Jul;31(4):713-721. doi: 10.1111/hae.70077. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Haemophilia. 2025. PMID: 40534395 Clinical Trial.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-clotting factor therapies for preventing bleeds in people with congenital hemophilia A or B.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Feb 27;2(2):CD014544. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014544.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38411279 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 28;11(11):CD003898. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003898.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29182799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Walsh CE, Jiménez-Yuste V, Auerswald G, Grancha S. The burden of inhibitors in haemophilia patients. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116(S01):S10–S17. - PubMed
-
- Hedner U. Recombinant activated factor VII: 30 years of research and innovation. Blood Rev. 2015;29(suppl 1):S4–S8. - PubMed
-
- Sevenfact [coagulation factor VIIa (recombinant)-jncw]. Prescribing information. HEMA Biologics . 2024. https://www.fda.gov/media/136610/download?attachment
-
- Cevenfacta [eptacog beta (activated)]. European Medicines Agency . 2022. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/cevenfacta
-
- Négrier C, Gomperts ED, Oldenburg J. The history of FEIBA: a lifetime of success in the treatment of haemophilia complicated by an inhibitor. Haemophilia. 2006;12:4–13.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
