Comparison of genotypes and phenotypes for von Willebrand factor gene variants using Japanese genome database
- PMID: 40765908
- PMCID: PMC12320396
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bvth.2025.100070
Comparison of genotypes and phenotypes for von Willebrand factor gene variants using Japanese genome database
Abstract
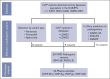
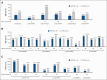
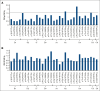
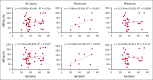
von Willebrand disease (VWD) is a common inherited bleeding disorder. The aim of this study was to determine the predicted disease states associated with various pathogenic von Willebrand factor (VWF) variants and their phenotypes using the largest Japanese whole-genome database. Of the 5857 VWF gene variants registered in the Japanese Multi-Omics Reference Panel (jMorp), variants with the following criteria were extracted: (1) caused protein abnormalities due to genetic alterations; (2) have already been detected and included in a database, including known association with VWD; and (3) highly likely pathogenic by in silico analysis. We measured VWF activity, antigen, propeptide, and collagen binding activity in stored plasma samples obtained from heterozygous carriers of the selected variants. A total of 29 VWF variants (26 single nucleotide and 3 small insertions/deletions) were detected, and 6 of these were found in Leiden Open Mutation Database. We obtained 43 plasma samples from individuals carrying these 29 variants as heterozygous. For the 43 variant carriers, their mean age was 43.0 years, and blood group was type O in 17 (39.5%). Analysis of these plasma samples showed low VWF levels (<50%) in 6 (14.0%). Low VWF levels were found in 2 of 8 of the nonsense (25%) and 4 of 31 of the missense variants (12.9%). Taking into consideration the limitation of using stored plasma samples, analysis of the jMorp indicated that most VWF gene variants with predicted pathogenic potential did not correlate with phenotypic expression. Our results supported incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity of the VWF gene variants.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: T.A. is an employee of BioMarin Pharmaceutical Japan K.K. H.I. has received speaker honoraria from Bayer, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk Pharma, and CSL Behring. A.M. is the holder of an endowed chair at the Department of Gene Research of Coagulation Disorders at Tokyo Medical University, which received funding from CSL Behring. R.M. has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, KM Biologics, Fujimoto Pharmaceutical, and CSL Behring. T.Y. has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, CSL Behring, Fujimoto Pharmaceutical, and Sanofi. Y.C. has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Pfizer, KM Biologics, Japan Blood Products Organization, Fujimoto Pharmaceutical, and CSL Behring. M.B. has received funding for research as a principal investigator from Chugai Pharmaceutical; and honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Pfizer, KM Biologics, Fujimoto Pharmaceutical, and CSL Behring. K.S. has received honoraria from Sanofi, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical, CSL Behring, Pfizer, and Japan Blood Products Organization. T.H. has received research grant from Sanofi; and honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, KM Biologics, Japan Blood Products Organization, and CSL Behring. K.A. has received honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, Pfizer, KM Biologics, Japan Blood Products Organization, Fujimoto Pharmaceutical, and CSL Behring. E.K. has received research grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical and CSL Behring; and honoraria from Chugai Pharmaceutical, Sanofi, Bayer, Takeda Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk Pharma, and CSL Behring. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic study of von Willebrand factor antigen levels ≤ 50 IU/dL identifies variants associated with increased risk of von Willebrand disease and bleeding.J Thromb Haemost. 2025 Aug;23(8):2410-2421. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2025.04.029. Epub 2025 May 12. J Thromb Haemost. 2025. PMID: 40368142
-
Clinical, Phenotypic and Genotypic Characteristics of Von Willebrand Disease in Afro-Caribbeans: Results From a Study in Martinique Island, French West Indies.Haemophilia. 2025 May;31(3):458-476. doi: 10.1111/hae.70003. Epub 2025 Mar 23. Haemophilia. 2025. PMID: 40123275 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Lenting PJ, Casari C, Christophe OD, Denis CV. von Willebrand factor: the old, the new and the unknown. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(12):2428–2437. - PubMed
-
- Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, Dini E. Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand's disease. Blood. 1987;69(2):454–459. - PubMed
-
- Sadler JE, Budde U, Eikenboom JC, et al. Update on the pathophysiology and classification of von Willebrand disease: a report of the Subcommittee on von Willebrand Factor. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4(10):2103–2114. - PubMed
-
- Seidizadeh O, Eikenboom JCJ, Denis CV, et al. von Willebrand disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2024;10(1):51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
