Analyzing 6211 unique variants in the upgraded interactive FVIII web database reveals novel insights into hemophilia A
- PMID: 40765911
- PMCID: PMC12320434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bvth.2025.100053
Analyzing 6211 unique variants in the upgraded interactive FVIII web database reveals novel insights into hemophilia A
Abstract
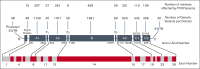
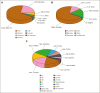
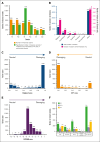
Hemophilia A is a rare genetic disease that occurs with mild, moderate, or severe phenotypes and involves dysfunctional or reduced amounts of plasma factor VIII (FVIII). Identifying causal genetic variants in the F8 gene is vital for patient care. Our original interactive MySQL database for FVIII in 2013 presented clinical data on 2014 unique FVIII variants in 5072 patients. Here, we expand our database almost threefold with a new total of 6211 unique FVIII variants in 10 064 patients, spanning 1529 of the 2351 FVIII residues (65%). We have also developed a new full-length FVIII structural model that incorporates both its crystal structure and its disordered B domain, which is not visible in available experimental structures. This enabled the assessment of these variants on FVIII. Of the 6211 unique F8 variants identified, 730 (12%) were associated with mild phenotypes, 526 (8%) with moderate phenotypes, 2509 (39%) with severe phenotypes, 53 (1%) with multiple severities, and 2393 (40%) with unreported phenotypes. Most variants occurred in the disordered B domain (1281 variants), followed by the A1, A2, and A3 domains (1130, 1071, and 923 variants, respectively) and the C1 and C2 domains (442 and 439 variants, respectively). Inhibitors were associated with 451 variants (7%). Our new structural analyses often revealed changes to the residue solvent surface accessibilities caused by many FVIII variants. The FVIII variant analyses are supported by similar observations in the structurally related FV protein. Our web-accessible FVIII database will enable easier and improved clinical analyses of FVIII genetic variants.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures






References
-
- Vehar GA, Keyt B, Eaton D, et al. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984;312(5992):337–342. - PubMed
-
- Shahani T, Covens K, Lavend'homme R, et al. Human liver sinusoidal endothelial cells but not hepatocytes contain factor-VIII. J Thromb Haemost. 2014;12(1):36–42. - PubMed
-
- Kalucka J, de Rooij LPMH, Goveia J, et al. Single-cell transcriptome atlas of murine endothelial cells. Cell. 2020;180(4):764–779.e20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
