Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Labeled Extracellular Vesicles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 40765940
- PMCID: PMC12323775
- DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.4c04888
Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Labeled Extracellular Vesicles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
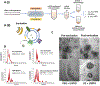
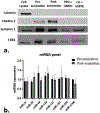
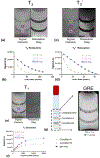
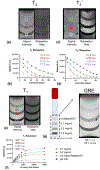
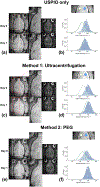
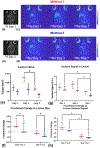
Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) offer a unique and promising alternative to direct cell injection as part of a cell-based therapy for stroke treatment. The development of labeling strategies is essential to identifying the initial biodistribution and clearance of EV-based therapeutics. In this study, hMSC-EVs were labeled with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Two methods of preparation were evaluated after EVs were sonicated in the presence of USPIO nanoparticle. The labeled EVs were purified by (1) ultracentrifugation only or (2) an extension of a harvesting approach that employs polyethylene glycol (PEG) to enrich EVs. Following in vitro assessment, labeled EVs were applied to an ischemic stroke model and imaged both immediately and longitudinally using MRI. In vitro assessment showed the EV characteristics after USPIO nanoparticle labeling. The PEG method exhibited a 3.6-fold enhancement in contrast using an equivalent USPIO concentration at 0.5 mg/mL and equivalent acquisition parameters (TE = 3.5 ms, TR = 5 s) when the dilution factor is considered. Sufficient USPIO nanoparticle labeling was achieved to visualize initial biodistribution and assess initial therapeutic potential. Taken together, simultaneous USPIO nanoparticle labeling and EV enrichment with PEG enhanced MRI contrast and improved outcomes with respect to delivery and ischemic stroke recovery.
Keywords: MRI; extracellular vesicles; human mesenchymal stem cells; preclinical ischemia; superparamagnetic iron oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Boudna M, Campos AD, Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Machackova T, Slaby O, Souckova K Strategies for labelling of exogenous and endogenous extracellular vesicles and their application for in vitro and in vivo functional studies. Cell Communication and Signaling 2024;22. 10.1186/s12964-024-01548-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dabrowska S, Del Fattore A, Karnas E, Frontczak-Baniewicz M, Kozlowska H, Muraca M, et al. Imaging of extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells using fluorescent and magnetic labels. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2018;13:1653–64. 10.2147/IJN.S159404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
