This is a preprint.
The polygenic architecture of hidradenitis suppurativa reveals signaling mechanisms that implicate epithelial remodeling
- PMID: 40766141
- PMCID: PMC12324615
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.25.25332168
The polygenic architecture of hidradenitis suppurativa reveals signaling mechanisms that implicate epithelial remodeling
Abstract
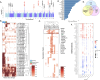
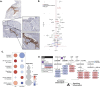
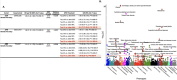
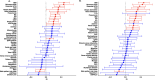
We sought to identify clinically relevant regulators of hair follicle inflammation by conducting a human genetic study of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a prevalent, understudied, inflammatory disease with limited effective treatments. We performed a GWAS with 6,300 cases and identified 12 independent risk loci. Epigenetic and transcriptomic analyses of HS risk variants defined cell-specific gene regulatory programs. We experimentally validated a coherent gene module defined by upregulated SOX9, CXCR4, and CD74 co-expression that maps to aberrant epithelial structures in the skin. Pharmacological inhibition of CXCR4 implicates CD74 mediated regulation of PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling to calibrate inflammation, proliferation and apoptosis in keratinocytes. We next used genome-wide methods to interrogate shared polygenic architecture and identified new clinically and mechanistically relevant disease associations, including another condition that involves aberrant hair follicle remodeling, male pattern hair loss. Our results point towards CXCR4-CD74 signaling in HS and hair follicle homeostasis and suggest CXCR4 blockade as a new therapeutic strategy in HS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ito M. et al. , Wnt-dependent de novo hair follicle regeneration in adult mouse skin after wounding. Nature 447, 316–320 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Smahi A. et al. , The NF-κB signalling pathway in human diseases: from incontinentia pigmenti to ectodermal dysplasias and immune-deficiency syndromes. Human molecular genetics 11, 2371–2375 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
