This is a preprint.
Polygenic Hazard Score for Predicting Age-associated Risk of Alzheimer's Disease in European Populations: Development and Validation
- PMID: 40766162
- PMCID: PMC12324663
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.07.28.25332293
Polygenic Hazard Score for Predicting Age-associated Risk of Alzheimer's Disease in European Populations: Development and Validation
Abstract
Objectives: Polygenic hazard score (PHS) models can be used to predict the age-associated risk for complex diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this study, we present an improved PHS model for AD that incorporates a large number of genetic variants and demonstrates enhanced predictive accuracy for age of onset in European populations compared to alternative models.
Methods: We used the genotyped European Alzheimer & Dementia Biobank (EADB) sample (n=42,120) to develop and evaluate the performance of the PHS model. We developed a PHS model building on 720 genetic variants, including Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε2 and ε4 alleles. We used Elastic Net-regularized Cox regression approach to develop the PHS model.
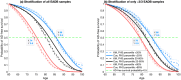
Results: The new PHS model (EADB720) improved prediction accuracy compared to alternative models in European populations, with the Odds Ratio OR80/20 from the highest quintile of risk (80th risk percentile and above) to the lowest quintile of risk (20th risk percentile and below) varying between 5.10 and 13.15 within the range of age of onset from 65 - 85 years. Our model also improved risk stratification across ε3/3 individuals of European ancestry (OR80/20 ranges from 1.95 to 3.52). It was also successfully validated in independent datasets (HUSK, DemGene and ADNI) by achieving OR80/20 up to 10.00 in each independent dataset.
Conclusion: Our EADB720 model significantly improves the accuracy of age-associated risk of AD across European populations (pval<0.03). Accurately predicting the age of onset of AD is of large clinical importance to implementing new AD medication and early intervention in clinical settings.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: Dr. Anders M. Dale is Founding Director, holds equity in CorTechs Labs, Inc. (DBA Cortechs.ai), and serves on its Board of Directors and Scientific Advisory Board. Dr. Dale is the President of J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI) and is a member of the Board of Trustees of JCVI. He is an unpaid consultant for Oslo University Hospital. The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California, San Diego in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies. Dr. Andreassen has received speaker fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Otsuka, Lilly, and Sunovion and is a consultant to Cortechs.ai. and Precision Health. Dr. Frei is a consultant to Precision Health. GS has participated in Advisory Board meetings for Roche, Eli-Lilly and Eisai regarding disease-modifying drugs for Alzheimer’s disease. GS has received honoraria for delivering lectures at symposia sponsored by Eisai and Eli-Lilly. Dan Rujescu served as consultant for Boehringer-Ingelheim and Janssen, received honoraria from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gerot Lannacher, Indorsia, Janssen and Pharmagenetix, received research/travel support from Angelini, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Janssen and Schwabe, and served on advisory boards of AC Immune, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Indorsia, Roche and Rovi. Timo Grimmer reported receiving consulting fees from Acumen, Advantage Ther, Alector, Anavex, Biogen, BMS; Cogthera, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Functional Neuromod.,Grifols, Janssen, Neurimmune, Noselab, Novo Nordisk, Roche Diagnostics, and Roche Pharma; lecture fees from Anavex, Cogthera, Eisai, Eli Lilly, FEO, Grifols, Pfizer, Roche Pharma, Schwabe, and Synlab; and has received grants to his institution from Biogen, Eisai and Eli Lilly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combating Genetic Heterogeneity for Polygenic Prediction of Susceptibility to Brain β-Amyloid Deposition: Beyond APOE.Neurol Genet. 2025 Jul 21;11(4):e200266. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000200266. eCollection 2025 Aug. Neurol Genet. 2025. PMID: 40703204 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Design of a Portable Birdcage via Meander Line Antenna (MLA) to Lower Beta Amyloid (Aβ) in Alzheimer's Disease.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2025 Apr 10;13:158-173. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2025.3559693. eCollection 2025. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2025. PMID: 40657533 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 10;2014(6):CD008782. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008782.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24913723 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Predicting cognitive decline: Deep-learning reveals subtle brain changes in pre-MCI stage.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 May;12(5):100079. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100079. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39920001 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
