Factors influencing the implementation of Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness (IMNCI) by nurses in Bhutan: A predictive correlational study
- PMID: 40766265
- PMCID: PMC12319682
- DOI: 10.33546/bnj.3816
Factors influencing the implementation of Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness (IMNCI) by nurses in Bhutan: A predictive correlational study
Abstract
Background: Integrated Management of Neonatal and Childhood Illness (IMNCI) is a critical strategy aimed at improving child health outcomes. In Bhutan, nurses play a frontline role in implementing IMNCI guidelines, yet factors influencing their implementation remain underexplored.
Objective: This study aimed to identify the predictors of IMNCI implementation among nurses in selected hospitals in Bhutan.
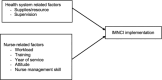
Methods: A correlational predictive design was used, involving 107 nurses from nine hospitals across Bhutan. Data on demographics, supplies/resources, supervision, attitude, workload, nurse management skills, and IMNCI implementation were collected between November and December 2023 through structured questionnaires. Multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to determine factors predicting IMNCI implementation.
Results: Nurse management skill was the only significant predictor of IMNCI implementation (β = 0.321, p <0.001), while other variables such as supplies/resources, supervision, attitude, years of service, training, and workload showed no significant predictive value. The model explained 16.8% of the variance in IMNCI implementation.
Conclusion: Nurse management skills play a pivotal role in effective IMNCI implementation in Bhutanese hospitals. However, the modest explanatory power suggests other factors may influence implementation, warranting further research to enhance child healthcare delivery through strengthened nurse leadership and systemic support.
Keywords: Bhutan; child health; implementation; management of childhood illness; nurse management skills; nurses; regression analysis; surveys and questionnaires.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrated management of childhood illness (IMCI) strategy for children under five.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jun 22;2016(6):CD010123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27378094 Free PMC article.
-
Experiences of registered nurses as managers and leaders in residential aged care facilities: a systematic review.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2011 Dec;9(4):388-402. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2011.00239.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2011. PMID: 22093388
-
Accreditation through the eyes of nurse managers: an infinite staircase or a phenomenon that evaporates like water.J Health Organ Manag. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1108/JHOM-01-2025-0029. Online ahead of print. J Health Organ Manag. 2025. PMID: 40574247
-
Barriers and facilitators to the implementation of lay health worker programmes to improve access to maternal and child health: qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 8;2013(10):CD010414. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010414.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24101553 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Abebe, A. M., Kassaw, M. W., & Mengistu, F. A. (2019). Assessment of factors affecting the implementation of integrated management of neonatal and childhood illness for treatment of under-five children by health professionals in health care facilities in Yifat Cluster in North Shewa Zone, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. International Journal of Pediatrics, 2019, 9474612. 10.1155/2019/9474612 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afolalu, T. D. (2020). Factors influencing the implementation of integrated management of childhood illnesses in selected health centers. International Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 1(6), 1027.
-
- Aggarwal, A. K., Gupta, R., Das, D., Dhakar, A. S., Sharma, G., Anand, H., Kaur, K., Sheoran, K., Dalpath, S., & Khatri, J. (2018). An alternative approach for supportive supervision and skill measurements of health workers for integrated management of neonatal and childhood illnesses program in 10 districts of Haryana. Indian Journal of Community Medicine, 43(1), 40–43. 10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_402_16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Samarrai, M. A. M., & Jadoo, S. A. A. (2018). Impact of training on practical skills of Iraqi health providers towards integrated management of neonate and child health-a multicentre cross-sectional study. Journal of Ideas in Health, 1(1), 1–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources