Immunomodulatory actions of tonifying polysaccharides: pharmacological effects, mechanisms and therapeutic applications
- PMID: 40766304
- PMCID: PMC12321766
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1640679
Immunomodulatory actions of tonifying polysaccharides: pharmacological effects, mechanisms and therapeutic applications
Abstract
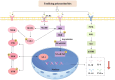
Tonifying polysaccharides, as a class of natural medicines, have attracted considerable interest due to their low toxicity, high safety profile, and excellent stability. Investigations have highlighted the significant impact of polysaccharides derived from Chinese medicinal herbs on the modulation of immune responses, significantly enhancing the functionality of immune organs such as the spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and intestines, stimulating immune cell proliferation and activation of T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells, and regulating the secretion and release of immune factors, thereby enhancing overall immune function. Tonifying polysaccharides, such as those found in medicinal herbs like ginseng and Astragalus, have demonstrated significant therapeutic effects in treating immune-mediated diseases, including anti-tumor, anti-autoimmune, and anti-viral activities. Despite the extensive literature published on the pharmacological effects, mechanisms, and therapeutic applications of Tonifying polysaccharides, there remains a lack of systematic organization and summarization. This review summarizes recent research findings on Tonifying polysaccharides within the field of immunomodulation. The research explores the immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic applications of polysaccharides, clarifying their roles in enhancing immune function and their potential in clinical treatments, and aims to establish a robust theoretical framework and scientific foundation for the investigation and practical application of Tonifying polysaccharides, drawing on the extensive research on their structural complexity, biological activities, and clinical applications, thereby promoting their development and application as immune-enhancing agents in traditional Chinese medicine and as vaccine adjuvants.
Keywords: Tonifying polysaccharides; immunomodulation; mechanisms; pharmacological effects; therapeutic actions.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Yi, Zhu, Yuan, Chen, Qiu, Shen, Song, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review on polysaccharides from Morinda officinalis How: Advances in the preparation, structural characterization and pharmacological activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jun 28;328:118090. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118090. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38521432
-
Recent Advances in the Mechanisms and Applications of Astragalus Polysaccharides in Liver Cancer Treatment: An Overview.Molecules. 2025 Jun 28;30(13):2792. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132792. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux: A systematic review on traditional use, and the chemical structures and pharmacological properties of polysaccharides and phenolic compounds in the roots.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jun 12;291:115148. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115148. Epub 2022 Feb 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35240238
-
Preparation technologies, structural features, and biological activities of polysaccharides from Mesona chinensis Benth.: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 May 23;326:117979. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117979. Epub 2024 Feb 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38412892
References
-
- Isidori AM, Hasenmajer V, Sciarra F, Venneri MA. Environmental Impact on Immune System. In: Pivonello R, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, editors. Environmental Endocrinology and Endocrine Disruptors. Springer International Publishing, Cham: (2022). p. 1–33. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-38366-4_13-1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources