Anti-IL5/IL-5 receptor therapies for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: an updated Systematic Review
- PMID: 40766318
- PMCID: PMC12321870
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1587158
Anti-IL5/IL-5 receptor therapies for eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: an updated Systematic Review
Abstract
Introduction: Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare necrotizing vasculitis characterized by eosinophilic inflammation that was traditionally treated with corticosteroids associated with other immunosuppressants. Over the last years different biological therapies targeting IL-5/IL-5 receptor have become available and have been employed to tackle this challenging condition. Aim of the present study is to synthesis the evidence on the clinical presentation of this disease and on the efficacy of the newly available therapeutic strategies.
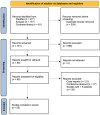
Methods: In June 2024 PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane library were searched for studies reporting on EGPA patients being treated by means of different anti IL-5 or anti eosinophils biological therapies. Risk of bias was assessed through the ROBINS-I and RoB2 tools according to study design. Proportion meta-analysis was employed to synthetize data on EGPA clinical manifestations, while data on treatment outcomes was analyzed descriptively due to the high heterogeneity.
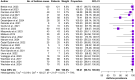
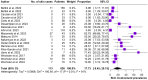
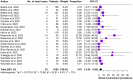
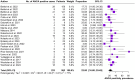
Results: The present systematic review included 25 studies on a total of 1131 patients. Asthma was present in 99.2% of the patients, Sinonasal involvement in 87.0% and ANCA positivity in 22.8%. The explored treatments consisted in Benralizumab 30 mg every 4 weeks, Mepolizumab 100 mg or 300 mg every 4 weeks and Reslizumab 3mg/Kg every 4 weeks. All the anti-IL-5/IL-5 receptor molecules proved efficacious in remission control and corticosteroid tapering.
Conclusion: The available data strongly suggests integrating anti IL-5/IL-5 receptor therapies into EGPA treatment strategies, to enhance patients' outcomes and reduce the long term side effects of prolonged corticosteroid therapy.
Keywords: EGPA; IL5; benralizumab; eosinophil; mepolizumab.
Copyright © 2025 Lazzeroni, Longoni, Schiavo, Bizzi, Brucato, Gramellini, Borin, Dragonetti, Gaffuri, Lentini, Maniaci, Mauro, Gidaro, Schroeder and Capaccio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures



References
-
- Greco A, Rizzo MI, De Virgilio A, Gallo A, Fusconi M, Ruoppolo G, et al. Churg-Strauss syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. (2015) 14:341–8. - PubMed
-
- Rios-Garces R, Prieto-Gonzalez S, Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Arismendi E, Alobid I, Penatti AE, et al. Response to mepolizumab according to disease manifestations in patients with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Eur J Intern Med. (2022) 95:61–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2021.08.021, PMID: - DOI - PubMed

