Synthetic and semi-synthetic antioxidants in medicine and food industry: a review
- PMID: 40766767
- PMCID: PMC12321848
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1599816
Synthetic and semi-synthetic antioxidants in medicine and food industry: a review
Abstract
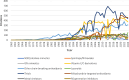
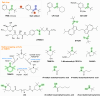
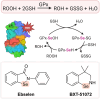
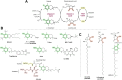
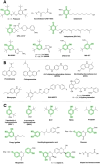
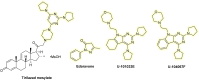
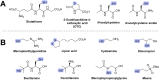
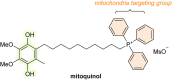
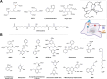
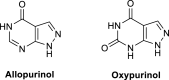
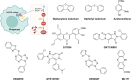
Oxidative stress is recognized as both a causative and contributing factor in many human diseases. As a result, significant research has been devoted to the development of synthetic and semi-synthetic antioxidants (ATs). This review summarizes the therapeutic potential of synthetic ATs, explores their possible clinical applications, and highlights novel structural modifications aimed at improving their pharmacological properties. Additionally, it presents ideas for refining current antioxidant testing methodologies. Despite the ongoing research, the therapeutic efficacy of synthetic ATs remains ambiguous for several reasons. These include the following: therapeutic benefits resulting from non-antioxidant mechanisms, insufficient dosage to elicit an antioxidant effect, poor oral bioavailability, a narrow therapeutic index, or toxicity that precludes clinical use. Nevertheless, some compounds, such as ebselen, edaravone, MitoQ10, and potentially N-acetylcysteine, have shown promising results. However, further studies are needed to confirm their efficacy and clarify whether their therapeutic effects are truly mediated through antioxidant mechanisms. Dietary antioxidants have achieved relatively higher clinical success, although their toxicity has also led to the withdrawal of some agents. One emerging therapeutic strategy involves inhibition of NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzymatic activity, with compounds such as ebselen, S17834, and GKT137831 showing potential across various disease models. Efforts to enhance antioxidant properties through molecular modifications, using advanced technologies such as prodrug strategies, nanotechnology, polymer complexation, targeted delivery systems, or conversion into inhalable formulations, have yielded variable success. Still, confirming the clinical relevance of newly developed antioxidants will require a paradigm shift in the testing approaches. Future studies must better define the molecular context of antioxidant action, including the following: which biomolecules are being protected, the specific radical species targeted, the tissue and subcellular distribution of the antioxidant, and how levels of endogenous antioxidants and reactive oxygen species (ROS) change post-administration (e.g., within the mitochondria). Despite extensive research, only a few synthetic antioxidants, such as edaravone, are currently used in clinical practice. Currently, no new antioxidant drugs are expected to receive regulatory approval in the near future.
Keywords: chelation therapy; free radical scavenging; oxidative stress; semi-synthetic antioxidants; synthetic antioxidants.
Copyright © 2025 Tauchen, Huml, Jurášek, Regenstein and Ozogul.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

