Quercetin Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Septic Liver Injury by Inhibiting the Activation of ROCK/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway
- PMID: 40766788
- PMCID: PMC12321602
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70757
Quercetin Improves Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Septic Liver Injury by Inhibiting the Activation of ROCK/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway
Abstract
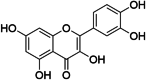
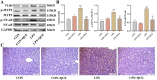
Quercetin (QUE) is a common flavonoid compound, found in fruits and vegetables, with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Nevertheless, the protective function and mechanisms of QUE in septic liver injury (SLI) caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) are still unknown. This study aimed to investigate the effect of QUE on SLI rats and the underlying mechanisms. Forty male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly assigned into four groups (n = 10 per group): control group (CON), control + QUE group (CON + QUE), LPS group (LPS), and LPS + QUE group (LPS + QUE). Rats were administered intragastrically with QUE or normal saline for one week, and LPS was administered on the last day to induce the sepsis model. The results showed that QUE reduced aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activities in SLI rats (both p < 0.05). Additionally, histopathological analysis demonstrated that QUE alleviated the liver lesions in SLI rats. Furthermore, QUE also improved the oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, showing the decrease of malonaldehyde (MDA), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18, and IL-6 and the increase of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in SLI rats (all p < 0.05). In addition, QUE decreased the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), phosphorylated myosin phosphatase target subunit (p-MYPT)-1, phosphorylated nuclear factor kappa-B (p-NF-κB), NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3), apoptosis-associated speck-like protein (ASC), caspase-1, and cleaved-caspase-1 in liver (all p < 0.05). These results suggested that QUE could be able to treat SLI partly via stimulating the ROCK/NLRP3 pathway.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; lipopolysaccharide; quercetin; rho kinase (ROCK); septic liver injury.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isorhamnetin protects against D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury in mice through anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammation, and anti-apoptosis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Aug 2;25(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04949-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40753249 Free PMC article.
-
Rutaecarpine Attenuates Monosodium Urate Crystal-Induced Gouty Inflammation via Inhibition of TNFR-MAPK/NF-κB and NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathways.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Jul;31(7):590-599. doi: 10.1007/s11655-025-4204-3. Epub 2025 May 8. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 40338445
-
Mechanism of Resveratrol on LPS/ATP-induced pyroptosis and inflammatory response in HT29 cells.Autoimmunity. 2024 Dec;57(1):2427094. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2024.2427094. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Autoimmunity. 2024. PMID: 39534992
-
Ginsenoside Rd protects against acute liver injury by regulating the autophagy NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 28;15(1):3569. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87991-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39875579 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Confers Protection against Sepsis-Related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome by Suppressing ROS/p38 MAPK Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2025 Jun 24. doi: 10.1007/s11655-025-3927-5. Online ahead of print. Chin J Integr Med. 2025. PMID: 40553253
References
-
- Ali, F. E. M. , Mohammedsaleh Z. M., Ali M. M., and Ghogar O. M.. 2021. “Impact of Cytokine Storm and Systemic Inflammation on Liver Impairment Patients Infected by SARS‐CoV‐2: Prospective Therapeutic Challenges.” World Journal of Gastroenterology 27, no. 15: 1531–1552. 10.3748/wjg.v27.i15.1531. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

