Correlation of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Critical Illness in Adults on Vancomycin: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 40766859
- PMCID: PMC12323880
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S537039
Correlation of Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Critical Illness in Adults on Vancomycin: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Background: Early risk-stratification in patients receiving vancomycin (VAN) is crucial but reliable markers are scarce. Herein, the correlates and determinants of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), an emerging inflammatory marker, with ICU admission in VAN-treated adults were investigated.
Methods: Demographic and clinical data for 295 adults treated with VAN at King Khalid University Hospital from January 2024 to February 2025 were retrospectively analyzed using Mann-Whitney U and Chi-square tests, Spearman rank correlation, regression analysis, effect size measures, and calculation of areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC).
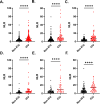
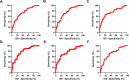
Results: NLR was significantly elevated in ICU compared to non-ICU patients (p <0.0001) and the proportion of ICU patients with elevated NLR was significantly higher than those with normal NLR (X 2 = 33.69, p <0.0001) irrespective of age or gender. In particular, ICU requirement was 2.49 and 2.54 times more prevalent in males and females with elevated NLR, respectively (p = 0.0002). Also, ICU admission was 4.25 and 4.40 times more likely when NLR was elevated in males and females, respectively (p = 0.0001). Notably, ICU admission was independently associated with a 9.65-unit increase in NLR (p = 0.0005) of which age, body mass index, and conjugated bilirubin were identified as independent predictors. Moreover, NLR showed good diagnostic ability for ICU requirement with AUC ranging from 0.71 to 0.78 (p <0.0001).
Conclusion: NLR is easily accessible, cost-effective, and demonstrates promising potential to complement existing markers for identifying high-risk patients and optimizing early intervention in critically ill adults receiving VAN therapy.
Keywords: ICU; NLR; inflammation; sepsis; vancomycin.
© 2025 Alfhili et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio(NLR), Triglyceride-Glucose Index (TyG), and TyG-derived indices with vitality decline in older adults in China: a study within the Integrated Care for Older People (ICOPE) framework.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Jul 30;24(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02671-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40739643 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
[Predictive value of plasma exosome count for the prognosis in septic patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Jul;36(7):687-692. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230717-00529. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39223881 Chinese.
-
Early intervention (mobilization or active exercise) for critically ill adults in the intensive care unit.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 27;3(3):CD010754. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010754.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29582429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel S, Preuss CV, Bernice F. Vancomycin. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 2025. ineligible companies. Disclosure: Charles Preuss declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Fidelia Bernice declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

