Multimodal Inhibition of Pectobacterium brasiliense Virulence by the Citrus Flavanone Naringenin
- PMID: 40767039
- PMCID: PMC12371876
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c04312
Multimodal Inhibition of Pectobacterium brasiliense Virulence by the Citrus Flavanone Naringenin
Abstract
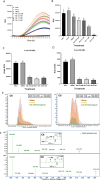
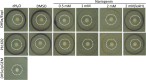
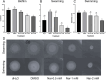
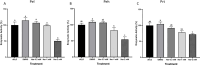
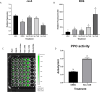
Naringenin, a flavanone from citrus, was studied for its ability to reduce virulence in Pectobacterium, a phytopathogen causing soft rot disease in crop plants. Naringenin downregulated quorum sensing (QS) and suppressed critical virulence determinants in Pectobacterium brasiliense Pb1692, including plant cell wall-degrading enzymes, bacterial motility, and biofilm formation, consequently reducing disease symptoms in two host plants. Molecular docking simulations revealed a plausible binding mode for naringenin within the QS protein ExpI, which were maintained during microsecond-long Molecular Dynamics simulations. These simulations provided atomic-scale insight into specific interactions and estimated binding free energies, supporting naringenin's QS inhibition mode of action. In contrast, S-adenosyl methionine, the natural ligand of ExpI, was unable to maintain a stable binding mode in the ExpI site during simulations. Beyond QS disruption, naringenin induced reactive oxygen species accumulation and compromised DNA repair, indicating a multimodal mechanism of action. Despite these promising findings, naringenin's limited aqueous solubility challenges practical applications.
Keywords: Pectobacterium brasiliense; ROS; molecular docking; molecular dynamics; naringenin; quorum sensing inhibitor.
Figures



References
-
- Gustafsson, J. ; Cederberg, C. ; Sonesson, U. ; Emanuelsson, A. . The Methodology of the FAO Study: Global Food Losses and Food Waste–Extent, Causes and Prevention–FAO, 2011; SIK Institutet för livsmedel och bioteknik, 2013.
-
- Ma B., Hibbing M. E., Kim H. S., Reedy R. M., Yedidia I., Breuer J., Breuer J., Glasner J. D., Perna N. T., Kelman A., Charkowski A. O.. Host range and molecular phylogenies of the soft rot enterobacterial genera pectobacterium and dickeya. Phytopathology. 2007;97(9):1150–63. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-97-9-1150. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tapia-Rodriguez M. R., Bernal-Mercado A. T., Gutierrez-Pacheco M. M., Vazquez-Armenta F. J., Hernandez-Mendoza A., Gonzalez-Aguilar G. A., Martinez-Tellez M. A., Nazzaro F., Ayala-Zavala J. F.. Virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exposed to carvacrol: alterations of the Quorum sensing at enzymatic and gene levels. Journal of cell communication and signaling. 2019;13(4):531–537. doi: 10.1007/s12079-019-00516-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

