Revictimisation Across Types of Interpersonal Violence: A Meta-Regression Analysis of PTSD and Associated Factors
- PMID: 40767146
- PMCID: PMC12326343
- DOI: 10.1002/smi.70079
Revictimisation Across Types of Interpersonal Violence: A Meta-Regression Analysis of PTSD and Associated Factors
Abstract
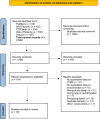
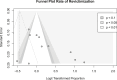
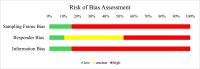
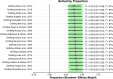
The literature has consistently demonstrated that being the victim of interpersonal violence increases the risk of future interpersonal violence (i.e., revictimisation). In this context, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is highly important since it has been investigated as a risk factor and consequence of revictimisation. The aim of the current study was to (a) compute a rate of revictimisation across types of interpersonal violence, and (b) examine which factors are associated with observed rates of revictimisation. We conducted a pre-registered systematic search in PubMed, APA PsycInfo, PTSDpubs, Web of Science, and Scopus, that resulted in N = 1286 individual records and n = 19 inclusions (PROSPERO ID: CRD42023446788). Criteria for inclusion were: adult human sample, assessment of PTSD symptoms that precedes assessment of interpersonal revictimisation, published in a peer-reviewed journal, longitudinal study design. Most studies focused on intimate partner revictimisation, followed by sexual revictimisation. The pooled rate of revictimisation was 39.2% for the overall group, and 53.4% for those experiencing intimate partner revictimisation. Only the proportion of females was positively associated with the observed rate of revictimisation. None of the other factors: presence of severe PTSD symptoms, mode of assessment (PTSD), type of sample, or duration of the follow-up period, were associated with the rates of revictimisation. We recommend the use of gold-standard assessment for PTSD, more representative and more clearly defined samples, and the development of a validated measure of revictimisation. For clinicians, we recommend paying attention to and providing psychoeducation about revictimisation and potential ways to prevent this. In sum, revictimisation is highly prevalent, but remains poorly understood. This gap may be addressed by rigorous methodological improvements (research) and psychoeducation (clinical practice).
Keywords: interpersonal violence; intimate partner violence (IPV); meta‐science; methodology; post‐traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); revictimisation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Stress and Health published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Epigenetic changes produced in women victims of intimate partner violence: A systematic review.Womens Health (Lond). 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17455057241290335. doi: 10.1177/17455057241290335. Womens Health (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39568400 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological and pharmacological interventions for posttraumatic stress disorder and comorbid mental health problems following complex traumatic events: Systematic review and component network meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2020 Aug 19;17(8):e1003262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003262. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Med. 2020. PMID: 32813696 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological therapies for women who experience intimate partner violence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 1;7(7):CD013017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013017.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32608505 Free PMC article.
-
Surveillance for Violent Deaths - National Violent Death Reporting System, 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico, 2022.MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025 Jun 12;74(5):1-42. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.ss7405a1. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2025. PMID: 40493548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . 2013. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM‐5™. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Publishing, a division of American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Bell, M. E. , Cattaneo L. B., Goodman L. A., and Dutton M. A.. 2008. “Assessing the Risk of Future Psychological Abuse: Predicting the Accuracy of Battered Women's Predictions.” Journal of Family Violence 23, no. 1: 69–80. 10.1007/s10896-007-9128-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

