Quantitative HILIC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis of Glycosaminoglycans and Non-reducing End Carbohydrate Biomarkers via Glycan Reductive Isotopic Labeling
- PMID: 40767435
- PMCID: PMC12368834
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c02338
Quantitative HILIC-Q-TOF-MS Analysis of Glycosaminoglycans and Non-reducing End Carbohydrate Biomarkers via Glycan Reductive Isotopic Labeling
Abstract
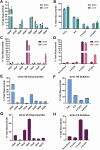
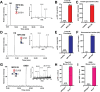
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear, heterogeneous polysaccharides expressed on all animal cells. Sulfated GAGs, including heparan sulfate (HS) and chondroitin/dermatan sulfate (CS/DS), are involved in numerous physiological and pathological processes; therefore, precise and robust analytical methods for their characterization are essential to correlate structure with function. In this study, we developed a method utilizing hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HILIC-Q-TOF-MS) and glycan reductive isotopic reducing end labeling (GRIL) for the quantitative compositional analysis of HS and CS/DS polysaccharides. Lyase-generated disaccharides and commercial standards were chemically tagged on the reducing end with aniline stable isotopes, thus enabling the absolute quantification of HS and CS/DS disaccharides in complex biological samples. In addition, we adapted this workflow, in conjunction with new synthetic carbohydrate standards, for the quantification of disease-specific non-reducing end (NRE) carbohydrate biomarkers that accumulate in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS), a subclass of lysosomal storage disorders. As a proof of concept, we applied this method to measure NRE biomarkers in patient-derived MPS IIIA and MPS IIID fibroblasts, as well as in cortex tissue from a murine model of MPS VII. Overall, this method demonstrates improved sensitivity compared to previous GRIL-LC/MS techniques and, importantly, avoids the use of ion-pairing reagents, which are undesirable in certain mass spectrometry instrumentation and contexts. By combining the benefits of HILIC separation with isotopic labeling, our approach offers a robust and accessible tool for the analysis of GAGs, paving the way for advancements in understanding GAG structure and function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
4-plex quantitative glycoproteomics using glycan/protein-stable isotope labeling in cell culture.J Proteomics. 2025 Jan 6;310:105333. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2024.105333. Epub 2024 Oct 18. J Proteomics. 2025. PMID: 39426592
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
[Fast determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in human serum by cold-induced phase separation coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2025 Jul;43(7):756-766. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2024.11028. Se Pu. 2025. PMID: 40610770 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
High-throughput glycosaminoglycan extraction and UHPLC-MS/MS quantification in human biofluids.Nat Protoc. 2025 Apr;20(4):843-860. doi: 10.1038/s41596-024-01078-9. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Nat Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39543382 Review.
-
Fabricating mice and dementia: opening up relations in multi-species research.In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. PMID: 40690569 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Glycosaminoglycan-driven lipoprotein uptake protects tumours from ferroptosis.Nature. 2025 Aug;644(8077):799-808. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09162-0. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40500442
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

