Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on weight loss after bariatric surgery: a retrospective single-center study with a follow-up of 3 years
- PMID: 40768087
- PMCID: PMC12328490
- DOI: 10.1007/s00423-025-03755-z
Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on weight loss after bariatric surgery: a retrospective single-center study with a follow-up of 3 years
Abstract
Introduction: Obesity is a major global health concern, with bariatric surgeries commonly performed to achieve significant weight loss, reduce obesity-associated morbidity and improve quality of life. The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted daily routines, impacting physical activity and eating behaviors, potentially affecting weight outcomes. This study aims to evaluate whether the COVID-19 lockdown influenced long-term weight loss outcomes in bariatric surgery patients by comparing three-year postoperative results between patients who had surgery immediately before the lockdown and those who had surgery up to two years earlier.
Methods: A retrospective cohort analysis was conducted at the University Hospital of Tuebingen. Patients were categorized into two groups: the pandemic group (surgery from October 2019 to March 2020) and the pre-pandemic group (surgery from October 2017 to March 2019). The primary outcome was weight loss, while secondary outcomes included cholesterol levels, HbA1c, and long-term complications like reflux, gallstones, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Follow-up assessments were conducted at 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, and 3 years.
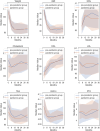
Results: A total of 194 patients were analyzed. Sleeve gastrectomy was performed in 72% of cases, and gastric bypasses in 28%. No significant differences were found between groups in demographics, surgical technique distribution, or follow-up rates. Weight, BMI, and excess weight loss were comparable between the two groups, with stabilization observed between 88 and 90 kg and 30–32 kg/m² from one to three years post-surgery. Complication rates and laboratory parameters (cholesterol, HbA1c, parathyroid hormone) showed no significant differences between the groups.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic did not significantly affect long-term weight loss outcomes or metabolic parameters in bariatric surgery patients up to three years postoperatively. These findings suggest that despite lifestyle disruptions due to the lockdown bariatric surgery remains effective for sustained weight management.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; COVID-19; Management; Pandemic; Quarantine; Weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: All research was performed to ethical standards of the declaration of Helsinki and all amendments. All patients provided written consent for anonymous data collection. Conflict of interest: There are no conflicts of interest. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Angrisani L, Ferraro L, Santonicola A, Palma R, Formisano G, Iovino P (2021) Long-term results of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity: 105 patients with minimum follow-up of 15 years. Surg Obes Relat Dis 17(4):727–736 - PubMed
-
- Courcoulas AP, Daigle CR, Arterburn DE (2023) Long term outcomes of metabolic/bariatric surgery in adults. BMJ 383:e071027 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

