IRX3 controls a SUMOylation-dependent differentiation switch in adipocyte precursor cells
- PMID: 40769964
- PMCID: PMC12328774
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62361-1
IRX3 controls a SUMOylation-dependent differentiation switch in adipocyte precursor cells
Abstract
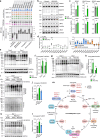
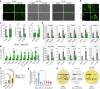
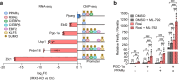
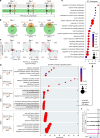
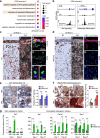
IRX3 is linked to predisposition to obesity through the FTO locus and is upregulated during early adipogenesis in risk-allele carriers, shifting adipocyte fate toward fat storage. However, how this elevated IRX3 expression influences later developmental stages remains unclear. Here we show that IRX3 regulates adipocyte fate by modulating epigenetic reprogramming. ChIP-sequencing in preadipocytes identifies over 300 IRX3 binding sites, predominantly at promoters of genes involved in SUMOylation and chromatin remodeling. IRX3 knockout alters expression of SUMO pathway genes, increases global SUMOylation, and inhibits PPARγ activity and adipogenesis. Pharmacological SUMOylation inhibition rescues these effects. IRX3 KO also reduces SUMO occupancy at Wnt-related genes, enhancing Wnt signaling and promoting osteogenic fate in 3D cultures. This fate switch is partially reversible by SUMOylation inhibition. We identify IRX3 as a key transcriptional regulator of epigenetic programs, acting upstream of SUMOylation to maintain mesenchymal identity and support adipogenesis while suppressing osteogenesis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



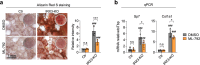
References
-
- Maes, H. H. M., Neale, M. C. & Eaves, L. J. Genetic and environmental factors in relative body weight and human adiposity. Behav. Genet.27, 325–351 (1997). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

