Structural basis of fast N-type inactivation in Kv channels
- PMID: 40770100
- PMCID: PMC12460158
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-09339-7
Structural basis of fast N-type inactivation in Kv channels
Abstract
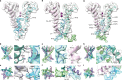
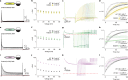
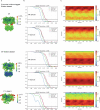
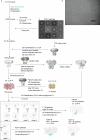
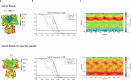
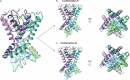
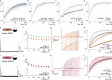
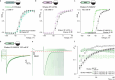
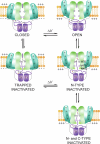
Action potentials are generated by opening of voltage-activated sodium (Nav) and potassium (Kv) channels1, which can rapidly inactivate to shape the nerve impulse and contribute to synaptic facilitation and short-term memory1-4. The mechanism of fast inactivation was proposed to involve an intracellular domain that blocks the internal pore in both Nav5,6 and Kv7-9 channels; however, recent studies in Nav10,11 and Kv12,13 channels support a mechanism in which the internal pore closes during inactivation. Here we investigate the mechanism of fast inactivation in the Shaker Kv channel using cryo-electron microscopy, mass spectrometry and electrophysiology. We resolved structures of a fully inactivated state in which the non-polar end of the N terminus plugs the internal pore in an extended conformation. The N-terminal methionine is deleted, leaving an alanine that is acetylated and interacts with a pore-lining isoleucine residue where RNA editing regulates fast inactivation14. Opening of the internal activation gate is required for fast inactivation because it enables the plug domain to block the pore and repositions gate residues to interact with and stabilize that domain. We also show that external K+ destabilizes the inactivated state by altering the conformation of the ion selectivity filter rather than by electrostatic repulsion. These findings establish the mechanism of fast inactivation in Kv channels, revealing how it is regulated by RNA editing and N-terminal acetylation, and providing a framework for understanding related mechanisms in other voltage-activated channels.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

