Green synthesis of Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles using sugarcane juice for magnetic hyperthermia applications
- PMID: 40770212
- PMCID: PMC12328811
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-11998-5
Green synthesis of Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles using sugarcane juice for magnetic hyperthermia applications
Abstract
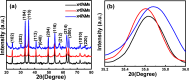
In this study, ecofriendly un-doped (0%), 5%, and 9% Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles were synthesized using sugarcane juice as reducing agents. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the high purity and crystalline nature of the undoped and Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was used to investigate the surface functional groups involved during the reducing and capping process. The internal structure of the particles was examined using high resolution transmission electron microscope (HRTEM). The particles exhibited semi-spherical shapes, with mean particle size of 9.3, 9.5 and 13.5 nm for the 0, 5 and 9% Mn-doped samples, respectively. The magnetic properties of the nanoparticles were measured by studying the magnetic field dependence of magnetization at 300 K and 2 K up to 4 T. The samples displayed hysteretic behavior characteristic of ferromagnetic materials at 2 K and typical superparamagnetic features at 300 K. The magnetic heating properties under AC magnetic fields were investigated to assess the feasibility of the synthesized NPs for magnetic hyperthermia application. The specific absorption rate (SAR) values of the iron oxide nanoparticles increased with the Mn-doping level. The results suggest that the green synthesis of un-doped and Mn-doped iron oxide nanoparticles holds promising potential for magnetic hyperthermia treatment.
Keywords: Green synthesis; Hyperthermia; Iron oxide; Nanoparticles; Sugarcane; Superparamagnetic.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Gour, A. & Jain, N. K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol.47, 844–851 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Jeevanandam, J., Chan, Y. S. & Danquah, M. K. Biosynthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles. ChemBioEng Rev.3, 55–67 (2016).
-
- Gebre, S. H. Bio-inspired Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: The Key Role of Phytochemicals. Journal of Cluster Science at (2022). 10.1007/s10876-022-02276-9
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

