Relationship Between the Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio and 28-Day Overall Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Pulmonary Embolism: A Retrospective Analysis of the MIMIC-IV Database
- PMID: 40770911
- PMCID: PMC12332334
- DOI: 10.1177/10760296251366420
Relationship Between the Lactate-to-Albumin Ratio and 28-Day Overall Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Pulmonary Embolism: A Retrospective Analysis of the MIMIC-IV Database
Abstract
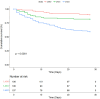
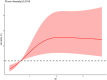
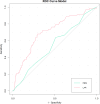
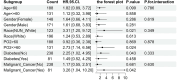
BackgroundThe lactate-to-albumin ratio (LAR) has prognostic value in various clinical conditions, but its association with mortality in pulmonary embolism (PE) remains unclear. This study aims to investigate the relationship between LAR and 28-day all-cause mortality in PE patients.MethodsThis retrospective observational study used MIMIC-IV database, with 28-day mortality as the primary endpoint. Adjusted Cox models were used to assessed the LAR-mortality association, with subgroup analyses for stability. Kaplan-Meier curves estimated mortality across LAR tertiles. Restricted cubic spline(RCS) analysis evaluated nonlinearity. Receiver operating characteristic curves(ROC) and reclassification metrics were used to compare the predictive performance of LAR with the Pulmonary Embolism Severity Index (PESI).ResultsAmong the 319 included patients, 72 (22.6%) died within 28 days of admission. Non-survivors had significantly higher LAR levels. In adjusted Cox models, elevated LAR was independently associated with increased 28-day mortality risk. Kaplan-Meier curves showed significant survival differences across LAR tertiles. RCS analysis revealed a dose-response relationship with an inflection point around LAR 0.67. The ROC curve's C-statistic, validated by the DeLong test, highlights the superior performance of the LAR model, while the positive Integrated Discrimination Improvement and Net Reclassification Improvement values demonstrate its additional prognostic value over the PESI model. Subgroup analysis confirmed consistent findings across different patient groups.ConclusionElevated LAR was positively correlated with 28-day all-cause mortality in PE patients, maintaining prognostic value across subgroups. LAR showed potential as a practical prognostic indicator for PE risk stratification, warranting prospective validation and exploration of its clinical utility in PE management.
Keywords: MIMIC-IV database; lactate/Albumin ratio; mortality; prognosis; pulmonary embolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between the lactate to albumin ratio and all-cause mortality in cardiac arrest patients: an analysis of the MIMIC-IV database.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 5;30(1):712. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02986-6. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40765007 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the lactate-to-albumin ratio in critically ill chronic heart failure patients with sepsis: insights from a retrospective cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 15;12:1593524. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1593524. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40735448 Free PMC article.
-
Association between international normalized ratio-to-albumin ratio and mortality in critically ill patients with gastrointestinal bleeding: a retrospective MIMIC-IV database study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 11;25(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04179-1. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40790158 Free PMC article.
-
Sex as a prognostic factor for mortality in adults with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 20;3(3):CD013835. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013835.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40110896
-
Catheter-directed therapies for the treatment of high risk (massive) and intermediate risk (submassive) acute pulmonary embolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 8;8(8):CD013083. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013083.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35938605 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

