Ambroxol confers neuroprotection against scopolamine-induced Alzheimer's-like pathology by modulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cognitive deficits via Nrf-2/JNK/GSK-3β signaling pathways
- PMID: 40771195
- PMCID: PMC12325200
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1607289
Ambroxol confers neuroprotection against scopolamine-induced Alzheimer's-like pathology by modulating oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cognitive deficits via Nrf-2/JNK/GSK-3β signaling pathways
Abstract
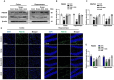
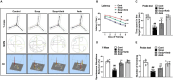
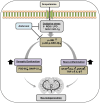
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common and costly chronic progressive neurodegenerative disorder, with the highest impact on public health worldwide. Pathological hallmarks of AD include progressive cognitive decline and memory impairment, dominantly mediated by oxidative neurodegeneration. Oxidative stress is commonly recognized as a key factor in the pathophysiological progression of AD. Despite significant advancements, a definitive and effective therapeutic intervention for AD remains elusive. In this study, we investigate the neuroprotective potential of ambroxol (Amb), known for its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Given ambroxol's potential neuroprotective effects, we explore the underlying molecular mechanisms, explicitly examining its role in attenuating scopolamine-induced oxidative stress-mediated activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, as well as its modulation of Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β) signaling, which is a key contributor to neuroinflammation, synaptic dysfunction and neurodegeneration. AD pathology is induced by scopolamine administration, leading to excessive lipid peroxidation (LPO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, which leads to a decline in critical antioxidant proteins, including nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). However, ambroxol treatment effectively attenuated oxidative stress by reducing the production of reactive oxidative species while restoring the expression of key antioxidant proteins. Similarly, ambroxol attenuated oxidative stress-induced JNK activation and modulated Akt and GSK-3β alterations. Immunofluorescence and western blot analyses revealed that ambroxol attenuated reactive gliosis by suppressing the expression of GFAP and Iba-1, alongside the downregulation of key pro-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1β, TNF-α, and phosphorylated NF-κB (p-p65). Scopolamine also compromised synaptic integrity and induced deficits in memory formation and spatial learning. In contrast, ambroxol promoted synaptic integrity by upregulating the expression of SNAP-23 and PSD-95, thereby ameliorating scopolamine-induced impairments in spatial learning and memory.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; ambroxol; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress; scopolamine; synaptic dysfunction..
Copyright © 2025 Ahmad, Choe, Ahmad, Park and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
MOK was employed by the company Alz-Dementia Korea Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Empagliflozin and memantine combination ameliorates cognitive impairment in scopolamine + heavy metal mixture-induced Alzheimer's disease in rats: role of AMPK/mTOR, BDNF, BACE-1, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun;33(6):3479-3498. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01755-5. Epub 2025 May 5. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40325262 Free PMC article.
-
Saikosaponin C ameliorates tau-related pathology by modulating oxidative stress and MAPK axis in Alzheimer's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Aug 29;352:120221. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120221. Epub 2025 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40588144
-
Melatonin Rescue Oxidative Stress-Mediated Neuroinflammation/ Neurodegeneration and Memory Impairment in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Mice Model.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019 Jun;14(2):278-294. doi: 10.1007/s11481-018-9824-3. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30478761
-
Decoding the Role of Neurotrophins in Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3-Beta Regulation in Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;62(7):8603-8623. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04776-x. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40014269 Review.
-
Preclinical evidence and potential mechanisms of tanshinone ⅡA on cognitive function in animal models of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 11;16:1603861. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1603861. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40717971 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

