Advancements in multi-omics research to address challenges in Alzheimer's disease: a systems biology approach utilizing molecular biomarkers and innovative strategies
- PMID: 40771197
- PMCID: PMC12325291
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1591796
Advancements in multi-omics research to address challenges in Alzheimer's disease: a systems biology approach utilizing molecular biomarkers and innovative strategies
Abstract
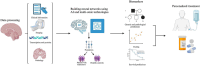
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a growing global challenge, representing the most common neurodegenerative disorder and affecting millions of lives. As life expectancy continues to rise and populations expand, the number of individuals coping with the cognitive declines caused by AD is projected to double in the coming years. By 2050, we may see over 115 million people diagnosed with this devastating condition. Unfortunately, while we currently lack effective cures, there are preventative measures that can slow disease progression in symptomatic patients. Thus, research has shifted toward early detection and intervention for AD in recent years. With technological advances, we are now harnessing large datasets and more efficient, minimally invasive methods for diagnosis and treatment. This review highlights critical demographic insights, health conditions that increase the risk of developing AD, and lifestyle factors in midlife that can potentially trigger its onset. Additionally, we delve into the promising role of plant-based metabolites and their sources, which may help delay the disease's progression. The innovative multi-omics research is transforming our understanding of AD. This approach enables comprehensive data analysis from diverse cell types and biological processes, offering possible biomarkers of this disease's mechanisms. We present the latest advancements in genomics, transcriptomics, Epigenomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, including significant progress in gene editing technologies. When combined with machine learning and artificial intelligence, multi-omics analysis becomes a powerful tool for uncovering the complexities of AD pathogenesis. We also explore current trends in the application of radiomics and machine learning, emphasizing how integrating multi-omics data can transform our approach to AD research and treatment. Together, these pioneering advancements promise to develop more effective preventive and therapeutic strategies soon.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s biomarkers; CRISPR; biomarkers; genomics; machine learning and radiomics; metabolomics; multi-omics; proteomics; radiomics.
Copyright © 2025 Cardillo, Katam and Suravajhala.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabricating mice and dementia: opening up relations in multi-species research.In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. PMID: 40690569 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Supervised Parametric Learning in the Identification of Composite Biomarker Signatures of Type 1 Diabetes in Integrated Parallel Multi-Omics Datasets.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 22;12(3):492. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030492. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540105 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

