Association between the oxidative balance score and testosterone deficiency in males: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 40771217
- PMCID: PMC12325012
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1577823
Association between the oxidative balance score and testosterone deficiency in males: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Testosterone deficiency is a prevalent condition among males and warrants greater attention. The balance between oxidative and antioxidant capacity plays a critical role in testosterone deficiency.
Methods: This study conducted a secondary analysis using data from three cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2011-2016). The oxidative balance score (OBS) and testosterone levels were derived from interview data and laboratory measurements. Weighted logistic regression was employed to explore the relationship between OBS and testosterone deficiency. Subgroup analyses, sensitivity analyses, and p-value for interaction were also performed.
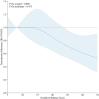
Results: The analysis encompassed a cohort of 3,578 participants who met the eligibility criteria. The prevalence of testosterone deficiency among participants was 23.69%. OBS was inversely correlated with testosterone deficiency, with each unit increase in OBS associated with a 3% reduction in the risk of testosterone deficiency (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99). The highest OBS group exhibited a 38% lower risk of testosterone deficiency (OR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.40 to 0.96) Compared to the lowest OBS group. Furthermore, lifestyle OBS was also negatively correlated with testosterone deficiency. In, subgroup analyses, the inverse association between OBS and testosterone deficiency was most pronounced in subgroups characterized by educational background beyond high school, PIR > 3, and absence of hypertension or diabetes.
Conclusion: Higher OBS was inversely correlated with testosterone deficiency in males. This study underscores the importance of comprehensive antioxidant approaches, particularly lifestyle OBS, in male testosterone deficiency.
Keywords: NHANES; dietary; lifestyle; oxidative balance score; testosterone deficiency.
Copyright © 2025 Zhuge, Zheng, Ji, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of oxidative balance lifestyle factors in reducing female infertility risk: insights from a population-based study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 19;16:1444832. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1444832. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40612439 Free PMC article.
-
Association between oxidative balance score and rheumatoid arthritis in female: a cross-sectional study.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Apr 6;24(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03066-3. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38582833 Free PMC article.
-
Association of oxidative balance score with the risk of all-cause and CVD mortality in younger US adults with diabetes.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 29;15(1):3609. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88132-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39875577 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ortega-de Los Ríos L, Getino L, Galán B, García JL, Luengo JM, Chamizo-Ampudia A, et al. Unlocking testosterone production by biotransformation: engineering a fungal model of aspergillus Nidulans strain deficient in steroid 11α-hydroxylase activity and expressing 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzyme as proof of concept. Biomol Ther. (2024) 14:1502. doi: 10.3390/biom14121502 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous