Comparative Efficacy and Recurrence of Combination Therapies in Keloid Management: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
- PMID: 40771257
- PMCID: PMC12327581
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000007048
Comparative Efficacy and Recurrence of Combination Therapies in Keloid Management: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Combination therapies are increasingly recognized in keloid management, which has been challenging due to high recurrence and variable individual responses. This Network Meta-Analysis (NMA) aimed to identify the most effective combinations with the lowest recurrence rates.
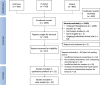
Methods: The protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024594922). Relevant Randomized Controlled Trials (RCT) evaluating all combination therapies for keloid were extracted from Cochrane, PubMed, and Scopus, until January 7, 2025.
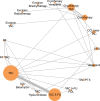
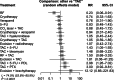
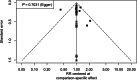
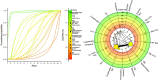
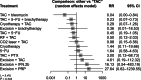
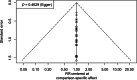
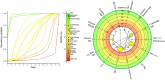
Results: A total of 1398 cases from 22 RCTs comparing different treatment combinations for keloid were included. The NMA revealed that only combinations involving Triamcinolone Acetonide (TAC) and 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) displayed significantly higher efficacy than TAC monotherapy: TAC + 5-FU + Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL) (RR 2.98; 95% CI: 1.26 to 7.02) and TAC + 5-FU (RR 1.43; 95% CI: 1.05 to 1.93). The lowest recurrence rates were found in TAC + bleomycin (RR 0.04; 95% CI: 0.00 to 0.84) and TAC + 5-FU + brachytherapy (RR 0.23; 95% CI: 0.07 to 0.73). No other combinations showed statistically significant differences. Funnel plot analysis revealed no publication bias.
Conclusions: Combination therapies, particularly TAC + 5-FU with PDL or brachytherapy, and TAC + bleomycin, outperform TAC alone in efficacy and recurrence reduction. These findings support tailored, multimodal approaches for optimal keloid management and improved patient outcomes.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Laser therapy for treating hypertrophic and keloid scars.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD011642. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011642.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161591 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- McGinty S, Siddiqui WJ. Keloid. StatPearls; 2023. Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507899/. Accessed January 16, 2025. - PubMed
-
- Bijlard E, Kouwenberg CA, Timman R, et al. Burden of keloid disease: a cross-sectional health-related quality of life assessment. Acta Derm Venereol. 2017;97:225–229. - PubMed
-
- Sadiq A, Khumalo NP, Bayat A. Genetics of keloid scarring. In: Téot L, Mustoe TA, Middelkoop E, et al., eds. Textbook on Scar Management: State of the Art Management and Emerging Technologies. Springer; 2020:61–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
