The expression profiles and roles of microRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism
- PMID: 40771283
- PMCID: PMC12325018
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1565385
The expression profiles and roles of microRNAs in cardiac glucose metabolism
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous, non-coding RNAs, that have been implicated in cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies have suggested that dysregulated miRNAs accumulate in the heart and may be associated with impaired cardiac glucose metabolism. However an inconsistent direction of expression was observed in the current available literature. The aim of this study was to characterize miRNA expression profiles associated with glucose metabolism, and to explore their potential as biomarkers for glucose metabolism disorders in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM).
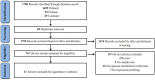
Methods: A systematic search of electronic databases, including Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library, was conducted until October 1, 2024. Studies reporting on miRNAs expression profiles that regulate glucose metabolism in the heart were selected for inclusion. Pooled results were presented as log10 odds ratios (logORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), using random-effect models. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on species, region, and sample source. Analyses by species focused specifically on humans and mice. The quality of included articles was assessed using the modified Diagnostic Accuracy Study 2 (QUADAS-2) tool. All workflows, including abstract screening, full-text review, data extraction, and quality assessment, were independently performed by two reviewers.
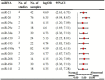
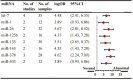
Results: A total of 47 eligible articles were included in this study, identifying 70 dysregulated miRNAs. Further analysis revealed that compared with the non-DCM group, the DCM group exhibited differential miRNA expression, with 12 miRNAs consistently upregulated and 8 consistently downregulated. Among these miRNAs, miR-199a (logOR 4.59; 95% CI: 3.02-6.15) was the most upregulated and frequently reported (n=7 studies), while let-7 (logOR 4.48; 95% CI: 2.41-6.55) was the most downregulated (4 studies). Subgroup analysis indicated that miRNA-21 was the most upregulated in cardiac tissue, and miRNA-133 was the most downregulated in cardiomyocytes. Additionally, miRNA-21 was found to be the most upregulated across different species. In the region subgroups, miRNA-199a and miRNA-503 were the most upregulated and downregulated in Asian countries, whereas miRNA-378 was the most dysregulated in non-Asian countries.
Conclusion: In summary, this study identified 20 consistently dysregulated miRNAs assocaited with myocardial glucose metabolism. Six dysregulated miRNAs, including miRNA-199a, let-7, miRNA-21, miRNA-133, miRNA-503 and miRNA-378, have potential as candidate miRNA biomarkers of glycometabolism in the heart. These findings require further validation in future larger-scale studies.
Keywords: biomarker; glucose metabolism; heart; miRNAs; systematic review.
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Qian and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
MicroRNAs as biomarkers in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A systematic review of recent clinical evidence.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022 Feb;213:107130. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107130. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35066247
-
The miRNA Mirage: How Close Are We to Finding a Non-Invasive Diagnostic Biomarker in Endometriosis? A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 17;19(2):599. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020599. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29463003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dutka DP, Pitt M, Pagano D, Mongillo M, Gathercole D, Bonser RS, et al. Myocardial glucose transport and utilization in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, left ventricular dysfunction, and coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2006) 48:2225–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.06.078, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhu L, Li D, Zhang X, Wan S, Liu Y, Zhang H, et al. Comparative efficacy on outcomes of c-cabg, opcab, and onbeat in coronary heart disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J surgery. (2023) 109:4263–72. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000715, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical