Pharmacological Therapy of HFrEF in 2025: Navigating New Advances and Old Unmet Needs in An Eternal Balance Between Progress and Perplexities
- PMID: 40771308
- PMCID: PMC12326316
- DOI: 10.15420/cfr.2024.37
Pharmacological Therapy of HFrEF in 2025: Navigating New Advances and Old Unmet Needs in An Eternal Balance Between Progress and Perplexities
Abstract
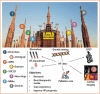
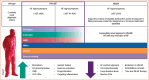
Recent advances in medical therapy have significantly improved the prognosis of patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The established four pillars of HFrEF treatment - β-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor- neprilysin inhibitors, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors - serve as the foundation for ongoing innovations in this domain. However, these represent only the starting point for the therapy and management of heart failure. New medications, new devices and improvements in the use of diuretic therapy are fundamental and recent advancements. This article aims to highlight the latest findings in HFrEF treatment. While emphasising the optimism these developments bring, the article also addresses the significant unresolved challenges that persist in the management of this syndrome, which remains a leading global cause of mortality, morbidity and poor quality of life with high use of resources and healthcare costs.
Keywords: Heart failure; angiotensin receptor–neprilysin inhibitors; diuretics; finerenone; gene therapy; sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors; vericiguat.
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Radcliffe Group Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources