Enjoyment of AI-generated stories blending art and science: impact on preschoolers' pro-environmental attitudes
- PMID: 40771322
- PMCID: PMC12325398
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1579510
Enjoyment of AI-generated stories blending art and science: impact on preschoolers' pro-environmental attitudes
Abstract
Background: This study explores the impact of artificial intelligence (AI)-generated stories that blend art and science on the development of pro-environmental attitudes and behaviors in preschoolers. AI-generated stories represent an innovative educational tool that leverages technology to create engaging, inclusive, and educational narratives. These stories can introduce young children to complex environmental concepts, fostering both cognitive understanding and emotional engagement with nature.
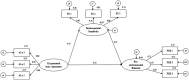
Hypotheses: The research examines three key hypotheses: (1) enjoyment of AI-generated stories will positively influence preschoolers' pro-environmental behavior, (2) enjoyment of AI-generated stories will positively influence preschoolers' environmental sensitivity, and (3) environmental sensitivity will mediate the relationship between story enjoyment and pro-environmental behavior.
Methods: The study included a total sample of 120 Chinese preschoolers from Upper Kindergarten () in Jiangmen City. Initially, children were introduced to AI-generated stories. After listening to the stories, their level of enjoyment was assessed. At the second time point, environmental sensitivity was measured through a game. At the third and final time point, children's pro-environmental behavior was assessed through a task designed to evaluate their actions and attitudes related to environmental conservation.
Results: Findings from this study suggest that preschoolers who enjoy AI-generated stories are more likely to display pro-environmental attitudes and behaviors, such as recycling and conserving resources. Furthermore, environmental sensitivity-a personal trait characterized by an emotional and cognitive connection to nature-was found to be a significant mediator in this relationship. Children who exhibit higher levels of environmental sensitivity are more likely to internalize the environmental messages embedded in the stories, translating enjoyment into meaningful, real-world actions.
Discussion: By combining the creative elements of storytelling with scientific content, AI-generated stories have the potential to become a powerful tool for fostering environmental awareness and responsibility in young children, contributing to the formation of environmentally responsible behaviors in future generations.
Keywords: AI-generated stories; Chinese preschool education; environmental sensitivity; preschoolers; pro-environmental behavior; storytelling enjoyment.
Copyright © 2025 Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Self-Set Goals: Autistic Adults Facilitating Their Self-Determination Through Digitally Mediated Social Stories.Autism Adulthood. 2025 Feb 5;7(1):25-38. doi: 10.1089/aut.2023.0063. eCollection 2025 Feb. Autism Adulthood. 2025. PMID: 40151659
-
Identifying and Addressing Bullying.2023 Dec 13. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Dec 13. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28722959 Free Books & Documents.
-
Education support services for improving school engagement and academic performance of children and adolescents with a chronic health condition.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 8;2(2):CD011538. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011538.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36752365 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad F., Rahim M. H. A., Razak A. A. A., Yusoff A. (2022). Metacognitive thinking and the effectiveness of the inquiry approach on value attitudes and motivation towards environmental education among primary school students in Malaysia. Adv. Human. Contemp. Stud. 3, 1–7. doi: 10.30880/ahcs.2022.03.01.001 - DOI
-
- Albrecht S., Zinn A. K., Grün B., Dolnicar S. (2024). Does enjoyment focus prevent proenvironmental behaviour? Ann. Tour. Res. 104:103714. doi: 10.1016/j.annals.2023.103714 - DOI
-
- Arn L., Huang E. (2024). Robots can do disgusting things, but also good things: fostering children’s understanding of AI through storytelling. ACM Trans. Comput. Educ. 24, 1–55. doi: 10.1145/3677613 - DOI
-
- Assary E., Oginni O. A., Morneau-Vaillancourt G., Krebs G., Peel A. J., Palaiologou E., et al. (2024). Genetics of environmental sensitivity and its association with variations in emotional problems, autistic traits, and wellbeing. Mol. Psychiatry 29, 2438–2446. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02508-6, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

