Fostering adolescent engagement in generative AI art therapy: a dual SEM-ANN analysis of emotional
- PMID: 40771325
- PMCID: PMC12327520
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1628471
Fostering adolescent engagement in generative AI art therapy: a dual SEM-ANN analysis of emotional
Abstract
Introduction: This study explores the application of generative artificial intelligence (AI) art in digital art therapy, focusing on how it influences adolescents' interest-driven participation. With mental health concerns rising among youth, understanding motivational mechanisms in AI-assisted therapeutic tools is both timely and essential.
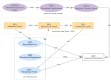
Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted with 444 junior and senior high school students in Hubei Province, China. The study integrated Emotional Design Theory and the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) to construct a predictive model. Structural equation modeling (SEM) and artificial neural network (ANN) analyses were employed to validate the model and identify key predictors of engagement.
Results: SEM results indicated that perceived usefulness (PU), perceived ease of use (PEOU), perceived fun (PF), and perceived trust (PT) significantly influenced users' attitudes toward use (ATT) (p < 0.001). ATT, PF, and PT were strong predictors of interest-driven participation, while the behavioral level had no direct effect on perceived enjoyment (PE). ANN analysis further highlighted ATT as the most influential predictor (100% normalized importance), notably exceeding PE (19.3%).
Discussion: These findings emphasize the importance of intuitive design, seamless interaction, and trust-building in sustaining adolescents' engagement with AI-based art therapy. The study provides a theoretical foundation for understanding interest formation in youth and offers practical implications for improving emotional design, digital therapeutic tools, and mental health interventions.
Keywords: TAM model; artificial neural network (ANN); digital art therapy; emotional design theory; generative AI painting; interest-driven.
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Qian and Bao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdullah F., Ward R., Ahmed E. (2016). Investigating the influence of the most commonly used external variables of TAM on students’ perceived ease of use (PEOU) and perceived usefulness (PU) of e-portfolios. Comput. Human Behav. 63, 75–90. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.014 - DOI
-
- Adams D. M., Mayer R. E., MacNamara A., Koenig A., Wainess R. (2012). Narrative games for learning: testing the discovery and narrative hypotheses. J. Educ. Psychol. 104:235. doi: 10.1037/a0025595 - DOI
-
- Adams D. A., Nelson R. R., Todd P. A. (1992). Perceived usefulness, ease of use, and usage of information technology: a replication. MIS Q. 16, 227–247. doi: 10.2307/249577 - DOI
-
- Alexiou A., Schippers M., Oshri I. (2012). Positive psychology and digital games: the role of emotions and psychological flow in serious games development. Psychology 3, 1243–1247. doi: 10.4236/psych.2012.312A183 - DOI
-
- Ali R. A., Soliman M., Weahama M. R., Assalihee M., Mahmud I. (2025). Investigating continuous intention to use metaverse in higher education institutions: a dual-staged structural equation modeling-artificial neural network approach. Smart Learn. Environ. 12:3. doi: 10.1186/s40561-024-00357-y - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources