The value of multiparametric MRI-based combined intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics in differentiating luminal and non-luminal molecular subtypes of breast cancer: a multicenter study
- PMID: 40771390
- PMCID: PMC12322763
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-2025-83
The value of multiparametric MRI-based combined intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics in differentiating luminal and non-luminal molecular subtypes of breast cancer: a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer remains the predominant contributor to global cancer-related morbidity and mortality in women. Luminal subtypes, accounting for approximately 70% of cases, demonstrate favorable prognoses through endocrine-targeted therapeutic regimens owing to hormone receptor positivity. Conversely, non-luminal breast cancer variants, including human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-enriched and triple-negative subtypes, exhibit aggressive biological characteristics, intrinsic endocrine therapy resistance, and require molecularly guided therapeutic strategies such as HER2-directed biologicals, platinum-based cytotoxic regimens, or radiation therapy. This study aims to evaluate whether preoperative multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics can effectively discriminate between luminal and non-luminal breast cancer subtypes.
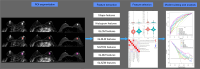
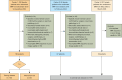
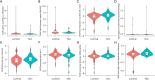
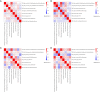
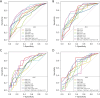
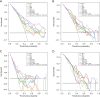
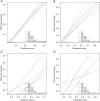
Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 305 female breast cancer patients. Center 1 (Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University) was randomly split into a training set (n=140) and an internal test set (n=59) in a 7:3 ratio, while Center 2 (Second Hospital of Lanzhou University) (n=67) and Center 3 (The Cancer Imaging Archive I-SPY1 trial) (n=39) served as external test sets 1 and 2, respectively. Tumor subtypes were classified as luminal or non-luminal based on estrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) status. Two radiologists performed manual tumor segmentation using 3D Slicer on multiparametric MRI sequences: dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE; phases 3 or 4), fat-suppressed T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Peritumoral regions were defined by a 3 mm expansion from the tumor volume of interest (VOI). For each sequence (intratumoral and peritumoral), 2,252 radiomics features were extracted using PyRadiomics. After Z-score normalization, features were selected through univariate analysis, correlation analysis, and simulated annealing. Eight radiomics models were constructed using random forest (RF), including intratumoral-only, combined intratumoral-peritumoral (3 mm), and multisequence fusion models. Performance was assessed using area under the curve (AUC), calibration curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: After feature selection, eight optimal radiomics features were used for model development. The combined DWI_Peri3 + T2WI_Peri3 + DCE_Peri3 RF model demonstrated superior performance, with AUCs of 0.819 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.748-0.889], 0.795 (95% CI: 0.676-0.915), and 0.771 (95% CI: 0.640-0.902) in training, internal validation, and external validation set 1, respectively. Among single-parameter models, T2WI_Peri3 RF showed the best classification performance (AUC =0.774, 95% CI: 0.698-0.849) for luminal vs. non-luminal differentiation.
Conclusions: The model constructed based on multiparametric MRI intratumor combined with peritumor radiomics features can better predict luminal and non-luminal types of breast cancer. This study can provide a reference basis for individualized treatment plans for breast cancer.
Keywords: Luminal and non-luminal breast cancer; multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (multiparametric MRI); peritumoral region; radiomics.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-2025-83/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
