Cadmium decreases human gingival fibroblast viability and induces pro-inflammatory response associated with Akt and MAPK pathway activation
- PMID: 40771401
- PMCID: PMC12325209
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2025.1583865
Cadmium decreases human gingival fibroblast viability and induces pro-inflammatory response associated with Akt and MAPK pathway activation
Abstract
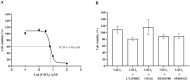
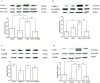
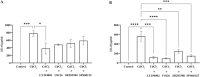
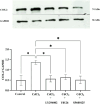
Smoking and particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) expose millions to cadmium (Cd), a toxic heavy metal linked to pro-inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and disease pathogenesis. In the oral cavity, chronic Cd exposure contributes to the progression of periodontal diseases and oral cancers. However, the direct effect of Cd on oral tissues and the underlying mechanisms remains unclear. This study explored the impact of environmentally relevant concentrations of Cd on human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs) by evaluating cell viability, pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion (IL-6 and IL-8), COX-2 expression, and the activation of key signaling pathways: Akt, ERK1/2, and JNK. Cd exposure significantly reduced HGF viability, elevated IL-6 and IL-8 secretion, and upregulated COX-2 expression. These effects were attenuated by inhibitors targeting Akt, ERK1/2, and JNK pathways. By integrating cytokine profiling, COX-2 expression, and inhibitor-based pathway analysis, our study provides mechanistic insights into how low-level Cd exposure triggers early inflammatory responses in gingival fibroblasts. Our findings reveal that Cd exerts pro-inflammatory and cytotoxic effects on HGFs, which may play a role as one of the factors in the pathogenesis of smoking-related oral diseases. Targeting Akt, ERK1/2, and JNK signaling pathways could offer therapeutic strategies to attenuate Cd-induced oral pro-inflammatory responses and tissue damage.
Keywords: cadmium; cyclooxygenase; fibroblasts; interleukin-6; interleukin-8.
Copyright © 2025 Parakaw, Srihirun, Sibmooh, Ruangsawasdi, Khemawoot and Vivithanaporn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Microbial Dysbiosis Driven by Periodontitis Facilitates Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 28;17(13):2181. doi: 10.3390/cancers17132181. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647479 Free PMC article.
-
2-O-methylmagnolol mitigates the generation of reactive oxidative stress and inflammaging in human gingival epithelial cells and fibroblasts with advanced glycation end products stimulation.J Dent Sci. 2025 Jul;20(3):1853-1860. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2025.04.022. Epub 2025 May 21. J Dent Sci. 2025. PMID: 40654450 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Pyroptosis of Gingival Fibroblasts in Peri-Implantitis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2025 Jul 21. doi: 10.1111/clr.70002. Online ahead of print. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2025. PMID: 40689757
-
MAPK, PI3K/Akt Pathways, and GSK-3β Activity in Severe Acute Heart Failure in Intensive Care Patients: An Updated Review.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Jul 10;12(7):266. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12070266. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40710791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Inflammation, Gut Microbiota, and Stress on Cognition and Oral Health Therapies.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2025;22(2):123-151. doi: 10.2174/0115672050361661250327061024. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2025. PMID: 40231539
References
-
- Bertuzzo C., Goodson J. M., Mager D., Pilatti G. L., Santos J. R., Silveira G. M., et al. (2003). “Salivary cadmium levels associated with smoking,” in IADR/PER disease mechanisms - molecular genetics and oral manifestations. Goteborg, Sweden.
-
- Bimonte V. M., Catanzaro G., Po A., Trocchianesi S., Besharat Z. M., Spinello Z., et al. (2024). The endocrine disruptor cadmium modulates the androgen-estrogen receptors ratio and induces inflammatory cytokines in luminal (A) cell models of breast cancer. Endocrine 83 (3), 798–809. 10.1007/s12020-023-03594-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

