Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 40771408
- PMCID: PMC12326305
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2025-1127
Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
Abstract
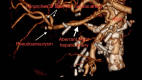
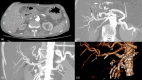
Pancreaticoduodenectomy is the standard surgical treatment for a range of malignant and some benign diseases. The mortality rate associated with this procedure has decreased to less than 3% in recent years, although the morbidity remains high at 6-40%. Common complications may include delayed gastric emptying, pancreatic fistula, intra-abdominal abscess, and gastrointestinal or intra-abdominal bleeding, among others. Bleeding and pseudoaneurysm formation are likely to be the most significant complications. This is a case report about gastrointestinal bleeding following a Whipple procedure from an aberrant hepatic artery originating from the superior mesenteric artery (SMA), treated by endovascular means. The SMA was cannulated under local anesthesia and direct puncture of the common femoral artery. Catheterization and angiogram of the aberrant right hepatic artery identified the pseudoaneurysm and bleeding site at its bifurcation. Coil embolization resulted in pseudoaneurysm occlusion and bleeding management. Hepatic perfusion was not affected as the main vasculature of the liver, namely the common hepatic artery, remained intact. The management of hemorrhage following pancreatectomy represents a significant challenge, particularly given the vulnerability of the patient cohort and the necessity for re-operation in an anatomically challenging environment. Endovascular intervention is the preferred method of treatment when applicable, as it can be performed under local anesthesia and is associated with less morbidity.
Keywords: endovascular management; hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm; post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Postoperative nutritional support after pancreaticoduodenectomy in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Mar 14;3(3):CD014792. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014792.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40084692
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Khalsa BS, Imagawa DK, Chen JI, Dermirjian AN, Yim DB, Findeiss LK. Evolution in the treatment of delayed postpancreatectomy hemorrhage: surgery to interventional radiology. Pancreas. 2015 Aug;44(6):953–8. - PubMed
-
- Leichtle SW, Kaoutzanis C, Mouawad NJ, Welch KB, Lampman R, Hoshal VL, et al. Classic whipple versus pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy in the ACS NSQIP. J Surg Res. 2013 Jul;183(1):170–6. - PubMed
-
- Campanile F, Maurea S, Mainenti P, Corvino A, Imbriaco M. Duodenal involvement by breast cancer. Breast J. 2012 Nov-Dec;18(6):615–6. - PubMed
-
- Wente MN, Veit JA, Bassi C, Dervenis C, Fingerhut A, Gouma DJ, et al. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage (PPH)–An International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) definition. Surgery. 2007 Jul;142(1):20–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
