Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- PMID: 40771411
- PMCID: PMC12326304
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2025-1109
Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
Abstract
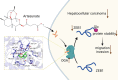
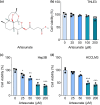
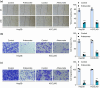
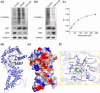
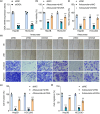
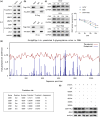
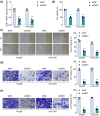
Metastasis remains a major challenge to improve the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Artesunate is an antimalarial drug that also has anti-cancer properties. Additionally, O-GlcNAcylation has been implicated in cancer progression. In this study, we investigated whether artesunate regulated HCC cell migration and invasion and explored its impact on protein O-GlcNAcylation. Cellular functions, including viability, migration, and invasion, were evaluated using the cell counting kit-8, scratch assay, and Transwell analysis. Molecular docking and biolayer interferometry were employed to assess the binding interaction between artesunate and OGA. Furthermore, the O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1 was examined using immunoprecipitation, cycloheximide chase assay, and immunoblotting. Our results demonstrated that artesunate significantly inhibited HCC cell viability, migration, and invasion. OGA expression was increased in HCC cells after artesunate treatment. Artesunate directly bound to OGA, and OGA knockdown reversed the inhibition of malignant behaviors induced by artesunate. Additionally, OGA suppressed the O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1 at the Ser670 site, decreasing protein stability. Knockdown of ZEB1 inhibited HCC cellular behaviors. In conclusion, artesunate inhibits HCC cell migration and invasion by binding to OGA, which removes the O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1 at the Ser670 site. These findings provide a new action mechanism for artesunate to treat HCC.
Keywords: O-GlcNAcylation; OGA; ZEB1; artesunate; hepatocellular carcinoma; invasion; migration.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sinomenine Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Inhibiting O-GlcNAcylation of SP1.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025 Sep;52(9):e70057. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.70057. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40671467
-
Nuclear factor IA-mediated transcriptional regulation of crystallin αB inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Mol Clin Oncol. 2025 Jun 20;23(2):72. doi: 10.3892/mco.2025.2867. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mol Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40599718 Free PMC article.
-
Protein O-GlcNAcylation in reproductive biology and the impact of metabolic disease.Hum Reprod Update. 2025 Jun 26:dmaf013. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaf013. Online ahead of print. Hum Reprod Update. 2025. PMID: 40574323
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
