Targeting MMR-deficient colorectal cancer with a potent small molecule UNI110
- PMID: 40771437
- PMCID: PMC12326383
- DOI: 10.1080/19768354.2025.2542172
Targeting MMR-deficient colorectal cancer with a potent small molecule UNI110
Abstract
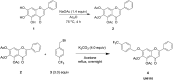
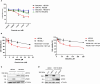
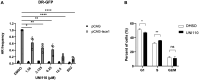
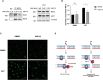
Mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency is a hallmark of microsatellite instability (MSI) in hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer, Lynch syndrome, contributing to resistance against conventional chemotherapy and posing a significant therapeutic challenge. In this study, we introduce UNI110, a novel small molecule derived from Baicalein, engineered for enhanced selectivity against MMR-deficient cancer cells. UNI110 exhibits a remarkable sevenfold increase in potency over Baicalein, demonstrating significantly lower IC50 values and heightened cytotoxic effects in MMR-deficient cell lines. Mechanistically, UNI110 selectively induces DNA damage in MMR-deficient cancer cells, ultimately resulting in cell death. Furthermore, UNI110 disrupts homologous recombination (HR) repair by inhibiting the MSH2-MSH3 complex, specifically blocking the interaction between MSH2 and EXO1, thereby impairing long-range end resection during double-strand break (DSB) repair. These findings establish UNI110 as a promising lead compound for the targeted treatment of MMR-deficient colorectal cancers, offering a potential breakthrough in overcoming chemotherapy resistance and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Baicalein; UNI110; end resection; homologous recombination; mismatch repair.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Chao JI, Su WC, Liu HF.. 2007. Baicalein induces cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT. Mol Cancer Ther. 6(11):3039–48. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0281. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
