Applications and advances of multi-omics technologies in gastrointestinal tumors
- PMID: 40771479
- PMCID: PMC12325369
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1630788
Applications and advances of multi-omics technologies in gastrointestinal tumors
Abstract
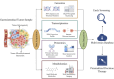
Gastrointestinal tumors pose a significant clinical challenge due to their high heterogeneity and the difficulties in early diagnosis. The article systematically reviews the latest advances in multi-omics technologies in gastrointestinal tumor research, focusing on their contributions to early screening, biomarker discovery, and treatment optimization. Genomics reveals genetic characteristics and heterogeneity of tumors; transcriptomics helps identify molecular subtypes and potential therapeutic targets; proteomics provides important information on core proteins and the immune microenvironment; and metabolomics offers promising biomarkers for early diagnosis. Furthermore, emerging fields such as epigenomics, metagenomics, and lipidomics, through the construction of multi-scale frameworks, have opened new paths for molecular subtyping and targeted therapy. By integrating these multi-dimensional data, multi-omics integration enables a panoramic dissection of driver mutations, dynamic signaling pathways, and metabolic-immune interactions. However, challenges such as data heterogeneity, insufficient algorithm generalization, and high costs limit clinical translation. In the future, the integration of single-cell multi-omics, artificial intelligence, and deep learning technologies with multi-omics may offer more efficient strategies for the precise diagnosis and personalized treatment of gastrointestinal tumors.
Keywords: biomarkers; early screening; gastrointestinal tumors; multi-omics technologies; single-cell genomics; treatment optimization.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Gao, Cheng, Qi and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Supervised Parametric Learning in the Identification of Composite Biomarker Signatures of Type 1 Diabetes in Integrated Parallel Multi-Omics Datasets.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 22;12(3):492. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030492. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540105 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of malignant digestive tract tumors: focusing on opportunities and challenges in endoscopy and pathology.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 9;23(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06428-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40205603 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing multi-omics and artificial intelligence: revolutionizing prognosis and treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1592259. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1592259. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40771801 Free PMC article.
-
Graph neural networks for single-cell omics data: a review of approaches and applications.Brief Bioinform. 2025 Mar 4;26(2):bbaf109. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf109. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40091193 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics approaches: transforming the landscape of natural product isolation.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jun 19;25(1):132. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01645-7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40537580 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

