Unrecognised rural-urban disparities in epidemiology of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in the representative area of China
- PMID: 40771524
- PMCID: PMC12322557
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjnph-2024-001087
Unrecognised rural-urban disparities in epidemiology of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in the representative area of China
Abstract
Background: The unexpectedly increased burden of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) continues in China, and the differences between rural and urban areas remain unclear. We aimed to clarify the prevalence and risk factors in rural areas of China.
Methods: This cross-sectional study used the most densely populated area with highly unbalanced development differences in China (Guangdong Province) as a representative sample, and multistage stratified random sampling was performed. The participants' demographic, socioeconomic and lifestyle data were collected. Fatty liver and liver stiffness were screened by FibroScan.
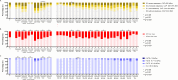
Results: A total of 7287 individuals were enrolled (rural: 2684; urban: 4603). The overall MAFLD prevalence was 35.7%, and MAFLD was higher among rural individuals (38.0% vs 34.4%, p<0.001) than urban individuals. Rural individuals had more severe hepatic fibrosis (fibrosis stage 3-4) overall (3.0% vs 1.3%) and among different sexes (male: 4.2% vs 2.0%; female: 1.5% vs 0.5%) (all p<0.05) than urban individuals. For both rural and urban individuals, lifestyle and dietary habits, including midnight snacks, dining out, and overeating salt, red meat and sugar, were associated with an increased risk of MAFLD, and drinking tea and consuming dietary fibres were associated with a decreased risk of MAFLD. However, midnight snacks and overeating red meat were associated with a higher risk of hepatic fibrosis only in urban individuals.
Conclusion: There is a surprisingly high burden of MAFLD in rural Guangdong, China, which implicates a lack of awareness among rural individuals and a warrant the need for disease counteraction strategies.
Trial registration number: ChiCTR2000033376.
Keywords: Dietary patterns; Metabolic syndrome.
Copyright © Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No, there are no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Investigation and analysis of mental health status of the older adult in western rural areas.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 16;13:1612600. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1612600. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40740371 Free PMC article.
-
Association between glycemic control and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in people with type 2 diabetes, stratified by chronic hepatitis B or C infection.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 31;18:17562848251356198. doi: 10.1177/17562848251356198. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40756178 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
