Advances in research on severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus
- PMID: 40771693
- PMCID: PMC12325320
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1622394
Advances in research on severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus
Abstract
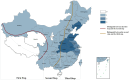
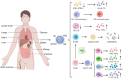
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is an acute infectious disease caused by the SFTS virus (SFTSV). Since the first reported case, SFTSV has spread globally, particularly in Asian regions such as China, South Korea, and Japan, with an increasing number of cases and a high mortality rate among severe patients. SFTSV is an RNA virus capable of rapid biological evolution through genetic mutations, reassortment, and homologous recombination. The disease primarily occurs in mountainous, forested, and hilly areas. Due to limited clinical research, the clinical characteristics and pathogenesis of SFTS remain incompletely understood. This review summarizes recent advances in the regional epidemiological characteristics, clinical features, genotyping, pathogenesis, and rapid detection methods of SFTSV.
Keywords: clinical features; genotype; pathogenesis; rapid detection; severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus.
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Li, Liu, Zhai, Dai and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

