A matched pilot cohort study of intravenous omadacycline in the treatment of severe pneumonia associated with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 40771696
- PMCID: PMC12325336
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1597860
A matched pilot cohort study of intravenous omadacycline in the treatment of severe pneumonia associated with carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
Background: Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB)-caused severe pneumonia is associated with high mortality rates, and treatment options are limited. Tetracyclines, including tigecycline and omadacycline, have in vitro activity against CRAB. We conducted this study to explore the efficacy of omadacycline in CRAB-caused severe pneumonia.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was performed by collecting data on severe CRAB-caused pneumonia cases treated with omadacycline or tigecycline at Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital from January 2022 to June 2024. A 1:1 propensity score-based matching design based on baseline characteristics was utilized. We compared the incidence of clinical response at day 14 or at the end of treatment (EOT) and other clinical outcomes between the two cohorts.
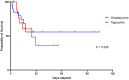
Results: A total of 40 patients were analyzed, with 20 patients in each cohort. The clinical success rate at day 14 or at the EOT was 65% (13/20) in the omadacycline group compared to 55% (11/20) in the tigecycline group. Both groups had an equal mortality rate, with 8 patients dying within 28 days. Development of tigecycline resistance was observed in one patient. The average duration of invasive mechanical ventilation, vasopressor, renal replacement therapy was also comparable in both groups. Adverse events occurred in 50% (10/20) of patients in the omadacycline group and 75% (15/20) in the tigecycline group, with coagulopathy being significantly lower in the omadacycline group (1/20, 5% vs. 7/20, 35%). Gastrointestinal events were reported in 10% (2/20) of the omadacycline group compared to 30% (6/20) in the tigecycline group. Abnormal liver function was observed in 9/20 patients (45%) in the omadacycline group and 6/20 patients (30%) in the tigecycline group.
Conclusion: This pilot study was the first to explore the efficacy and safety of omadacycline in CRAB-caused pneumonia. Omadacycline demonstrated comparable efficacy to tigecycline in this small pilot study in the treatment of CRAB-caused pneumonia and has a lower incidence of coagulopathy compared to tigecycline, suggesting it may be a viable option, for treating CRAB-caused severe pneumonia, but further prospective research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii; omadacycline; pneumonia; retrospective matched cohort study; tigecycline.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Chen, Hu, Gu, Kan, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Barrasa H., Morán M. A., Fernández-Ciriza L., Isla A., Solinís M. Á., Canut-Blasco A., et al. (2024). Optimizing antibiotic therapy for Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infections in critically ill patients: a pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic approach. Antibiotics (Basel). 13:553. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060553, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bone R. C., Balk R. A., Cerra F. B., Dellinger R. P., Fein A. M., Knaus W. A., et al. (1992). American college of chest physicians/society of critical care medicine consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 20, 864–874. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources