Regulated programmed cell death in acute lung injury: from pathogenesis to therapy
- PMID: 40771815
- PMCID: PMC12325065
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1630015
Regulated programmed cell death in acute lung injury: from pathogenesis to therapy
Abstract
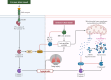
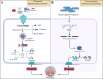
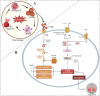
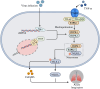
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a common, life-threatening lung disease with a high mortality rate, primarily associated with acute and severe inflammation of the lungs. There are many factors that lead to ALI, and abnormally advanced regulated programmed cell death (RCD) is considered to be an important process in the pathological process of ALI. Various forms of RCD have been discovered in recent years, including apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis and pyroptosis. Unlike necrosis, RCD is an active cell death mediated by a series of gene expression events that is essential for eliminating unnecessary and damaged cells as well as defense mechanisms. Previous studies have shown that RCD has a strong relationship with ALI. Therefore, it is important to describe the role of RCD not only to enhance our understanding of the pathophysiological processes of ALI, but also to improve the functional recovery after ALI. This review reviews the roles and mechanisms of various RCD (apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, ferroptosis and autophagy) in ALI, and discusses the associations among various types of RCD. The aim is to explore the molecular mechanism behind SALI and find new targets for the treatment of ALI. This review will help us understand the various functions and mechanisms of RCD in the pathological process of ALI, and help us to treat various ALI of unknown etiology.
Keywords: acute lung injury; acute respiratory distress syndrome; pathological mechanism; programmed cell death; treatment.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Chen, Liu, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
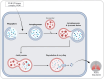
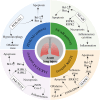
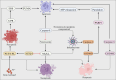
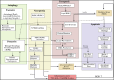
Similar articles
-
Beyond apoptosis: evidence of other regulated cell death pathways in the ovary throughout development and life.Hum Reprod Update. 2023 Jul 5;29(4):434-456. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmad005. Hum Reprod Update. 2023. PMID: 36857094 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated Cell Death-Targeted Ocular Nanomedicine.Acta Biomater. 2025 Aug 9:S1742-7061(25)00600-2. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2025.08.018. Online ahead of print. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40789529 Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNAs regulates cell death in osteosarcoma.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22592. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04440-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595878 Free PMC article.
-
Partial liquid ventilation for preventing death and morbidity in adults with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 23;2013(7):CD003707. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003707.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23881653 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

