Combination of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization and PD-1 inhibitor for treatment of unresectable head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an initial, short-term clinical experience in a single-center retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 40771818
- PMCID: PMC12325233
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1615440
Combination of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization and PD-1 inhibitor for treatment of unresectable head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an initial, short-term clinical experience in a single-center retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: This study investigated the clinical efficacy and safety of CalliSpheres® drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) combined with programmed death protein (PD)-1 inhibitors for treatment of unresectable head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
Methods: Clinical data of 31 patients with unresectable HNSCC were retrospectively analyzed. All patients received local treatment with DEB-TACE combined with systemic PD-1 inhibitor. Modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) criteria were used to evaluate the tumor response at 1, 3 and 6 months after the first treatment. Progression-free survival and overall survival were recorded. The changes in quality of life before and after treatment and adverse reactions during treatment were recorded.
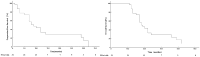
Results: Patients were treated with DEB-TACE 51 (average 1.65 ± 0.51) times. At 1, 3 and 6 months after the first treatment, objective response rate was 96.77%, 87.09% and 74.19%, and disease control rate was 100%, 96.77% and 83.87%, respectively. As of October 31, 2024, the mean follow-up was 21.71 ± 9.56 months, median survival time was 9.0 months, and the median progression-free survival was 19.0 months. The adverse reactions related to DEB-TACE were mainly fever, pain, nausea and vomiting; all of which were mild and relieved after symptomatic treatment. Three patients had mild skin ulceration in the embolic area, which healed after symptomatic treatment, and no serious complications such as ectopic embolism occurred. The adverse reactions associated with PD-1 inhibitor treatment were mainly fatigue, hypothyroidism and rash. Most of these were grade 1/2, three patients had grade 3 adverse reactions, but no grade 4 adverse reactions occurred. One month after the first treatment, the scores of physical function, emotional function and general health status increased, and the scores of pain, insomnia and anorexia decreased, and quality of life was significantly improved.
Discussion: Combination of DEB-TACE with PD-1 inhibitors is safe and effective for treatment of unresectable HNSCC, significantly improves quality of life, and warrants clinical promotion and application.
Keywords: camrelizumab; drug-eluting CalliSpheres® -beads; head and neck malignancies; squamous cell carcinoma; transarterial chemoembolization.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Gao, Li, Song, Li and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of TACE combined with lenvatinib and PD-1 Inhibitor in intermediate-stage HCC exceeding the up-7 criteria: a retrospective cohort study.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 12;16:1560750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1560750. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40574843 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of the Short-Term Efficacy and Safety between DEB-TACE and C-TACE in the Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a Retrospective Study.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241250315. doi: 10.1177/15330338241250315. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38773767 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization in the treatment for unresectable soft tissue sarcoma refractory to systemic chemotherapy: a preliminary evaluation of efficacy and safety.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Jan;144(1):157-163. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2530-3. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 28993945 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness of different transarterial embolization therapies alone or in combination with local ablative or adjuvant systemic treatments for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 21;12(9):e0184597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184597. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28934265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leeman JE, Li JG, Pei X, Venigalla P, Zumsteg ZS, Katsoulakis E. Patterns of treatment failure and postrecurrence outcomes among patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma after chemoradiotherapy using modern radiation techniques. JAMA Oncol. (2017) 3:1487–94. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0973, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

