The Drosophila Zinc Finger Protein Aef1 Colocalizes with Enhancers and Is Involved in the Transcriptional Regulation of Numerous Genes
- PMID: 40771843
- PMCID: PMC12322892
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.27556
The Drosophila Zinc Finger Protein Aef1 Colocalizes with Enhancers and Is Involved in the Transcriptional Regulation of Numerous Genes
Abstract
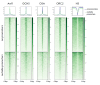
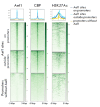
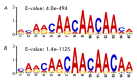
In our previous studies, we demonstrated that the Drosophila zinc finger protein Aef1 interacts with the SAGA DUB module. The Aef1 binding sites colocalize with the SAGA histone acetyltransferase complex and the dSWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, as well as the origin recognition complex (ORC). Aef1 predominantly localizes with the promoters of active genes (55% of all sites) and can be involved in transcriptional regulation. In this study, we showed that Aef1 binding sites in Drosophila S2 cells, located outside gene promoters, are nucleosome-depleted regions and colocalize with the SAGA, dSWI/SNF, and ORC complexes. Aef1 binding sites colocalize with the CBP protein and the H3K27Ac histone tag, which is considered to be an active enhancer mark. An RNA-Seq experiment was conducted in Drosophila S2 cells, both normal and with RNA interference targeting the Aef1 protein, to study the role played by the Aef1 protein in transcriptional regulation. The Aef1 protein was shown to affect the transcription of 342 genes, more than half of those (178 genes) containing Aef1 at their promoters or enhancers. Hence, we infer that the Aef1 protein is recruited to both promoters and enhancers and is involved, both directly and indirectly, in the regulation of the transcription of the respective genes.
Keywords: Aef1; CBP; H3K27Ac; ORC; SAGA; dSWI/SNF; enhancers.
Copyright ® 2025 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The Drosophila Zinc Finger Proteins Aef1 and CG10543 Are Co-Localized with SAGA, SWI/SNF, and ORC Complexes on Gene Promoters and Involved in Transcription Regulation].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2024 Jul-Aug;58(4):619-626. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2024. PMID: 39709566 Russian.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Orphanides G., Reinberg D., Cell. 2002;108(4):439–451.:10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00655-4. - PubMed
-
- Maksimenko O., Georgiev P.. Front Genet. 2014;5:28.:10.3389/fgene.2014.00028.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
