Extracellular Vesicles As a Source of Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnosis
- PMID: 40771849
- PMCID: PMC12322890
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.27591
Extracellular Vesicles As a Source of Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
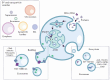
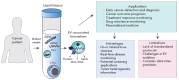
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are secreted by nearly all mammalian cells and play a major role in intercellular communication via the transport of various active biomolecules. In cancer, pathological EVs contribute to tumor progression by participating in metastasis, angiogenesis, and immune evasion. Recent advancements in EV research have revealed their potential as noninvasive biomarkers. This review addresses the latest advancements in EV isolation and characterization techniques, elucidates the molecular mechanisms underlying EV biogenesis, and examines their functional roles in cancer progression. Furthermore, we discuss emerging strategies that leverage EV profiling and molecular composition analysis, in conjunction with liquid biopsy technologies, offering possible breakthroughs in early cancer diagnosis and treatment monitoring. By synthesizing these insights, this review emphasizes the growing significance of EVs as versatile and powerful diagnostic tools in oncology.
Keywords: EVs; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; liquid biopsy; oncology.
Copyright ® 2025 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures
References
-
- Doyle L.M., Wang M.Z., Cells. 2019;8(7):727.:10.3390/cells8070727.
-
- Chuo S.T.-Y., Chien J.C.-Y., Lai C.P.-K.. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018;25(1):91.:10.1186/s12929-018-0494-5.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
