Comparative Analysis of Pioglitazone and Tirzepatide on Body Weight, Glucose Levels, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 40771859
- PMCID: PMC12325112
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S525690
Comparative Analysis of Pioglitazone and Tirzepatide on Body Weight, Glucose Levels, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a widespread metabolic illness that compromises cognitive function by inducing inflammation and oxidative damage. Diabetes mellitus is treated with many types of medications, including tirzepatide (TZP) and pioglitazone (PIO), which have also been shown to enhance cognitive deficits associated with the condition. This study intends to investigate the neuroprotective effects of TZP and PIO on type 2 diabetic mellitus (T2DM) via mitigating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, along with enhancing cognitive impairment in rats as models with T2DM.
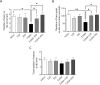
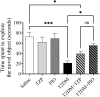
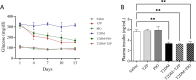
Methods: A total of six distinct groups of sixty albino rat males (n = 10) were allocated at random: Saline, TZP, PIO, T2DM, T2DM+TZP, and T2DM+PIO. Intramuscular doses of streptozotocin (50 mg/kg) and nicotinamide (120 mg/kg) precipitated T2DM. The TZP and PIO therapies persisted for a duration of 15 days. The survival percentage, body weight, behavioral assessments (Y-maze, novel object recognition (NOR)), glucose concentrations, inflammatory mediators tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), as well as oxidative stress biomarkers superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), malondialdehyde (MDA), and lipid peroxidation were evaluated following the conclusion of the treatments.
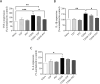
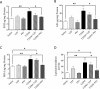
Results: The results demonstrate that diabetes decreased survival rates, body weight, cognitive function, increased glucose levels, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress. The TZP and PIO increased survival rates and cognitive function as well as decreased glucose levels, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in diabetic rats, with PIO demonstrating a more pronounced effect on neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, contrasted with TZP.
Discussion: This study concluded that TZP and PIO enhanced cognitive impairment in diabetic rats, with PIO demonstrating superior efficacy in contrast to TZP.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; diabetes; inflammation; insulin; oxidative stress; pioglitazone; tirzepatide.
© 2025 Alhowail et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tirzepatide mitigates cognitive decline in zebrafish model of type 2 diabetes mellitus induced by high-fat diet.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8861-8883. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03827-3. Epub 2025 Jan 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39873719
-
Human placental extract rescues hippocampal damage associated with cognitive impairment in diabetic male rats through antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and neuromodulatory activities.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jun 16;40(6):225. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01646-2. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40522516 Free PMC article.
-
Micheliolide mitigates diabetic nephropathy by modulating oxidative stress and inflammation in rats.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157025. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157025. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40712283
-
Impact of a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide on heart rate among patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and pairwise and network meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024 Feb;26(2):548-556. doi: 10.1111/dom.15342. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024. PMID: 37860884
-
Subcutaneously administered tirzepatide vs semaglutide for adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Diabetologia. 2024 Jul;67(7):1206-1222. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06144-1. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38613667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giri B, Dey S, Das T, Sarkar M, Banerjee J, Dash SK. Chronic hyperglycemia mediated physiological alteration and metabolic distortion leads to organ dysfunction, infection, cancer progression and other pathophysiological consequences: an update on glucose toxicity. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:306–328. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.157 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

