Analytical Techniques for the Determination of Paracetamol and Ibuprofen Combination
- PMID: 40771889
- PMCID: PMC12328053
- DOI: 10.1155/jamc/6822390
Analytical Techniques for the Determination of Paracetamol and Ibuprofen Combination
Abstract
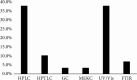
The fixed-dose combination (FDC) of ibuprofen (IBU) and paracetamol (PAR) has emerged as a preferred option in pain management, owing to its distinct practical advantages. Both drugs have well-documented efficacy and safety profiles, providing synergistic pain relief through complementary mechanisms of action. IBU not only offers central analgesic effects but also inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, particularly COX-1 and COX-2, thereby reducing prostaglandin synthesis at the site of pain to deliver both analgesic and anti-inflammatory benefits. Despite the growing use of this combination, a comprehensive review focusing on the analytical methods for its determination has not yet been published. This review aims to bridge that gap by presenting an extensive compilation of documented analytical methods for the quantification of IBU and PAR in both bulk and pharmaceutical formulations. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers and professionals seeking detailed insights into the diverse techniques employed for accurate and precise analysis of these FDCs. Through a systematic search of major scientific databases, including Science Direct, Springer Link, PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, the review identifies the most commonly utilized methods, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC), ultraviolet (UV)/Visible spectrophotometry, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC). Notably, HPLC and UV/Visible spectrophotometry were the most frequently reported, each accounting for 37.9% of studies. By consolidating these analytical approaches, this review highlights the state-of-the-art methodologies available for the determination of IBU/PAR FDCs and underscores its novel contribution as a definitive reference for future research and development in this field.
Keywords: determination; dosage form; ibuprofen; paracetamol.
Copyright © 2025 Imad O. Abu Reid et al. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pergolizzi J. V., Raffa R. B. The WHO Pain Ladder: Do We Need Another Step. Practical Pain Management . 2014;14(1):42–52.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous